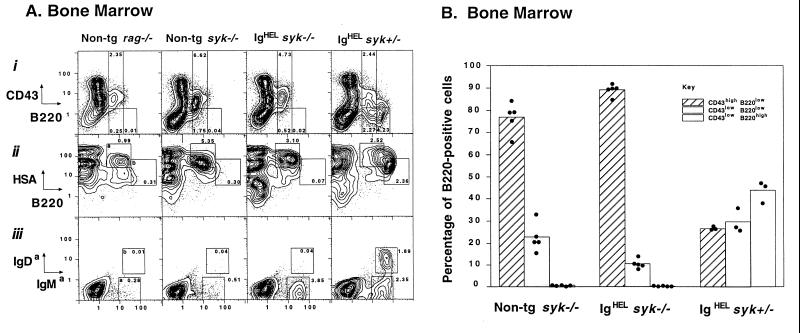
Figure 1.
Developmental arrest of Syk-deficient B cells in the bone marrow is not rescued by expression of rearranged Ig H + L transgenes encoding IgHEL. (A) B-cell development in bone marrow of nontransgenic rag−/−, nontransgenic syk−/−, and IgHEL-transgenic syk−/− and syk+/− chimeric mice, measured by two-color flow cytometry of cells stained for the indicated developmental markers. Windows in plots (ii–iii) are conventional for immature (a) and mature (b) B cells, and the frequency of cells are shown as a percentage of the total cells in the bone marrow. Plots of syk−/− and syk+/− bone marrows are each representative of six chimeras. (B) Histograms summarizing the percentage of B220-positive B-lineage cells in the bone marrow which are CD43hiB220lo (Hardy A–C); CD43loB220lo (Hardy D–E); and CD43loB220hi (Hardy F). Bars represent arithmetic means and dots the percentages from individual chimeras. Mean numbers of B220 cells present in the bone marrow from one femur and one tibia of nontransgenic syk−/−, IgHEL syk−/− and IgHEL syk+/− mice were 20.10 × 104 (SD = 7.60); 14.42 × 104 (SD = 1.79); and 17.50 × 104 (SD = 3.90), respectively (SD = standard deviation × 10−4).