Fig. 1.
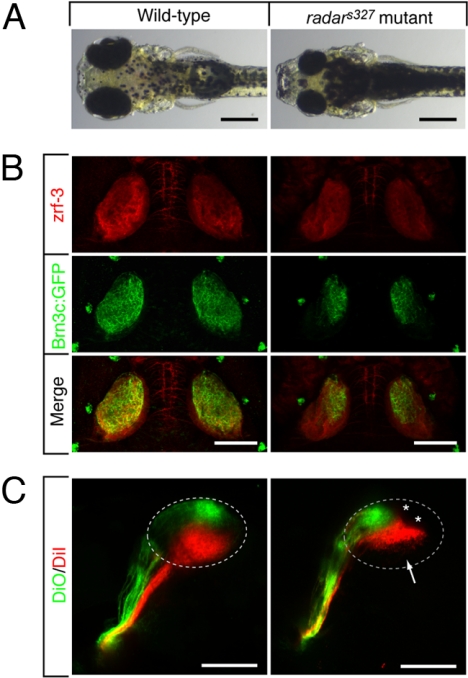
Morphological and retinotectal phenotypes of radars327. (A) Zebrafish radars327 mutants have small eyes and appear dark, because of a VBA defect (see text). Dorsal brightfield views of 7 dpf WT sibling and homozygous radars327 mutant larvae. (B) radars327 mutants lack ventral innervation of the optic tectum. Dorsal confocal projections of 7 dpf larvae show that innervating RGC axons (expressing Brn3c:mGFP) are confined to the dorsal tectum in the mutant. Costaining with a neuropil marker (zrf-3 antibody) reveals that the size of the tectum is similar in WT and mutant. (C) radars327 mutants have a compressed dorsal–ventral retinotectal map. Fixed WT and radars327 eyes (7 dpf) were injected with DiO (ventrally) and DiI (dorsally). Lateral confocal projections are shown. Arrow highlights ventral tectal region not innervated by RGCs in radars327; asterisks show positions of skin melanophores. (Scale bars: 300 μm in A, 100 μm in B and C.)