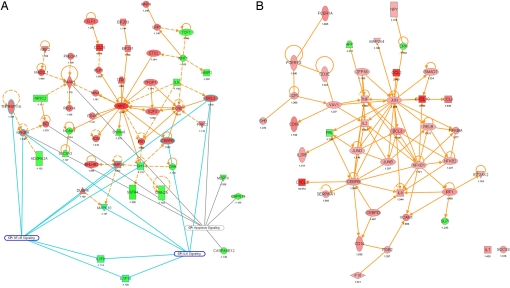
Fig. 3.
Ingenuity protein–protein interaction networks. The interaction map was derived by plotting interacting proteins involved in specific cellular functions: immune response, immune system development and function, cell signaling, cell cycle, cell growth, cell death and proliferation. Transcriptional information was projected onto the interaction map; up-regulated genes are depicted in shades of red, down-regulated genes in shades of green. Relevant pathways that feature modulated genes were indicated as well. (A) transcriptional networks modulated after consumption of midlog bacteria. From this interaction map, it can be seen that the up-regulated PARP1, MYC, and CCND1 are important nodes associated with the mentioned pathways. (B) transcriptional networks modulated after consumption of dead bacteria. Major nodes are proteins from the CEBP, JUN, and NFKB family but also proinflammatory TNF and IFN regulatory factor, IRF1.