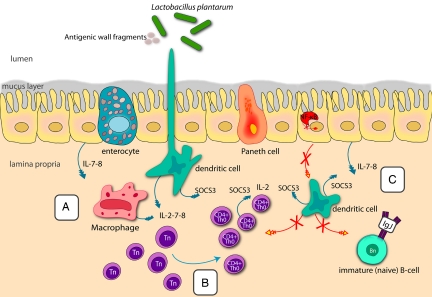
Fig. 4.
Proposed model of cellular proteins and processes associated with immune tolerance induced in the proximal small intestine of healthy adults after consumption of L. plantarum. (A and B) Because of up-regulation of factors such as A20 and IκBα and lack of p65 (RelA), no continuous NF-κB driven proinflammatory gene transcription is expected. Interleukins (blue arrows) are exclusively up-regulated during the interaction with dead bacteria (A) and are proposed to stimulate the maturation of CD4+ cells (B); overt stimulation by ILs is probably balanced by the suppressor SOCS3. (C) The crossed-out red arrows between IECs and dendritic, T and B cells indicate that no stimulatory or activating contact takes place between these cells through lack of expression of necessary genes such as BAFF, AID, IL-1, and TSLP.