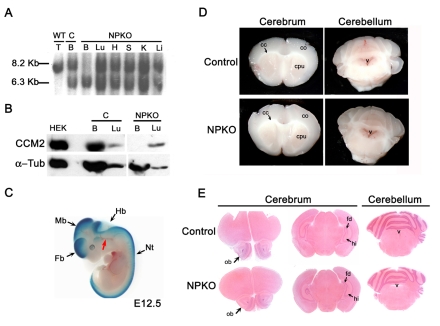
Fig. 2.
Conditional deletion of CCM2 from neuroglial precursors does not lead to major cerebrovascular defects. (A-C) Analysis of the specific inactivation of CCM2 in the neuroglial compartment. (A) Southern blot analysis using 12 μg of genomic DNA extracted from tissues at P8. DNA was digested by HindIII and hybridized with the external radiolabeled 3′ probe P2. The floxed allele (8.2 kb) in NPKO was recombined specifically within the brain of NPKO mice. A Ccm2–/flox brain from a littermate was used as a control for the absence of recombination (second lane from the left). The 6.3 kb and the 8.2 kb DNA fragments represent the Ccm2-deleted and floxed alleles, respectively. Note that the DNA fragment in the first lane is slightly lower than the floxed fragment and corresponds to the 8.13 kb wild-type allele. (B) Western blot analysis of CCM2 protein expression within the brain (100 μg protein lysates) and the lung (70 μg protein lysates) from NPKO mice and a control littermate at P8. CCM2 protein was not detected in NPKO brain lysates. Protein lysate from Ccm2-transfected HEK cells was used as a positive control (200 ng). Note that the second lane of the blot is free of sample. Immunoblotting for α-tubulin on the same blot was performed as a loading control. (C) β-galactosidase expression analysis on a E12.5 embryo obtained after crossing a nestin-Cre; Ccm2 floxed animal with a Rosa26R reporter line (genotype of the embryo: nestin-Cre; Rosa26R; Ccm2+/flox). Note that the blood vessels (red arrow) are not blue, demonstrating an absence of recombination in the ECs. (D,E) Analysis of the brains from NPKO and control mice. (D) Analysis of 2 mm-thick brain coronal sections from 2-month-old NPKO and control animals under a dissecting microscope, showing slices of the cerebrum (left panels) and the cerebellum (right panels). (E) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining on 10 μm paraffin-embedded brain sections from NPKO or control mice at P19. B, brain; C, control; cc, corpus callosum; co, cortex; cpu, caudate putamen; Fb, forebrain; fd, fascia dentata; H, heart; Hb, hindbrain; hi, hippocampus; K, kidney; Li, liver; Lu, lung; Mb, midbrain; Nt, neural tube; ob, olfactory bulb; S, spleen; T, toe; v, ventricle.