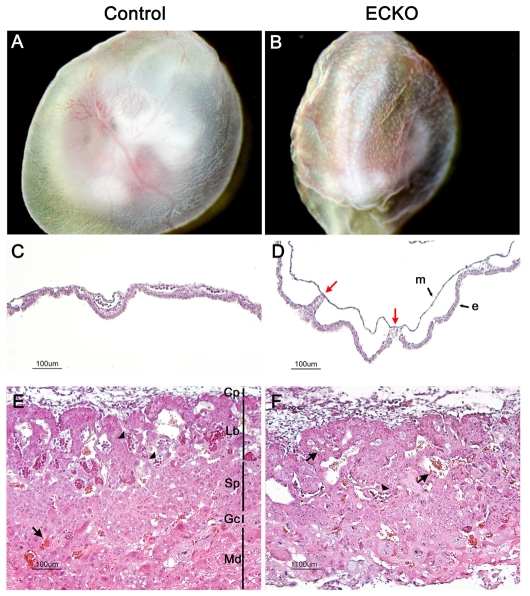
Fig. 4.
Vascular defects in extra-embyonic tissues in ECKO embryos at E10.5. (A,B) Newly dissected E10.5 ECKO YSs are easily distinguishable from control ones owing to their wrinkled surface and their immature vasculature, which remains in a honeycomb pattern. (C,D) H&E staining of E10.5 YS cross sections. Compared with the control YSs (C), the endodermal (e) and mesodermal (m) layers are rarely connected in the ECKO YSs [red arrows in panel (D)]. (E,F) Placenta histology in control (E) or ECKO (F) embryos at E10.5. Note the rare embryonic nucleated red blood cells (arrowheads) in the labyrinthine layer in the ECKO placenta, and the presence of maternal red blood cells (arrows). Cp, chorionic plate; Gc, giant cells; Lb, labyrinthine trophoblaste; Md, maternal decidua; Sp, spongiotrophoblast.