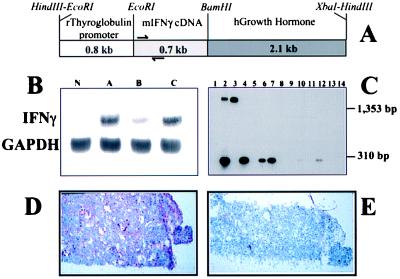
Figure 1.
Thyroid-specific expression of IFN-γ in transgenic mice. (A) Organization of thyr-IFN-γ transgene. The thyroglobulin promoter, IFN-γ cDNA, and growth hormone splice donor and acceptor sequences are indicated by rectangles. The primers used for reverse transcriptase–PCR are indicated by arrows. (B) Thyroidal expression of IFN-γ in normal C57BL/6 mice (N) and in the three transgenic lines (A, B, and C), as assessed by Northern blot analysis. (C) Expression of IFN-γ in thyroids and other tissues: water control (lane 1); genomic DNA from line A transgenic (lane 2); genomic DNA from normal C57BL/6 (lane 3); thyroid RNA from line A transgenic with (lane 4) and without (lane 5) reverse transcriptase; thyroid RNA from line B transgenic (lane 6), line C transgenic (lane 7), and normal C57BL/6 (lane 8); and RNA from liver (lane 9), lymph nodes (lane 10), salivary glands (lane 11), spleen (lane 12), brain (lane 13), and testicles (lane 14). Sizes of DNA standards, in base pairs, are indicated on the right. (D) Immunohistochemical analysis of the expression of IFN-γ by thyroid cells. (E) Control slide without addition of the primary antibody.