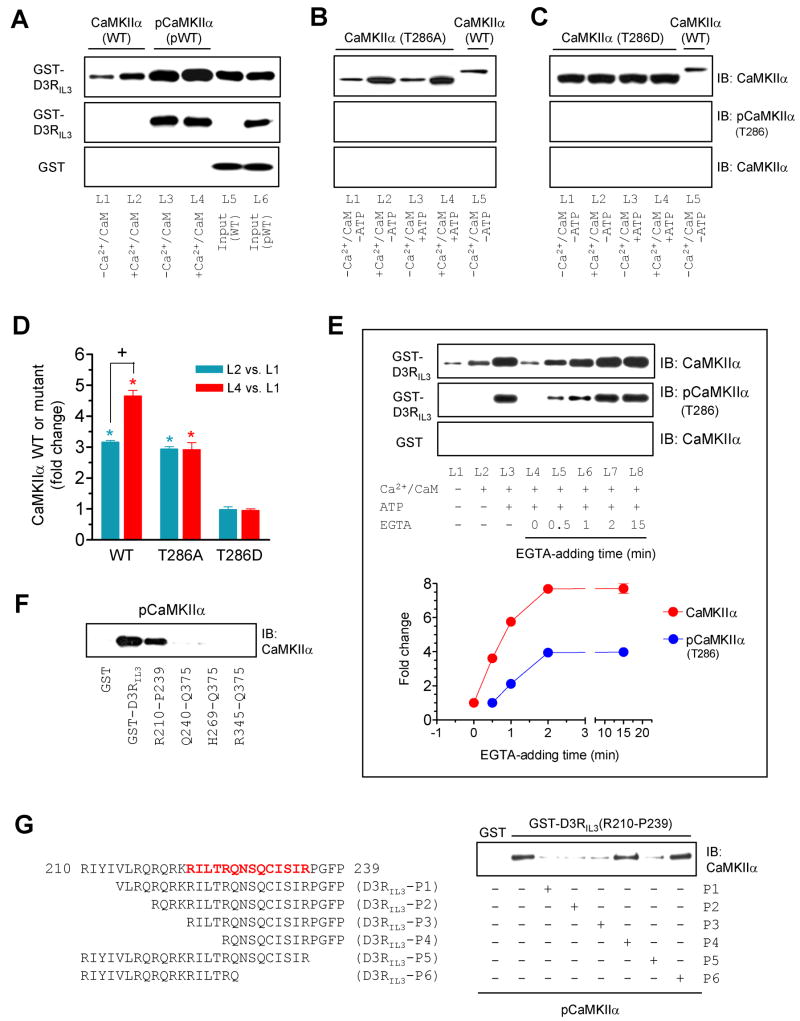
Figure 3. Influence of T286 autophosphorylation on the CaMKIIα-D3RIL3 binding.
(A–C) Binding of WT CaMKIIα/pCaMKIIα (A), mutant T286A (B), or mutant T286D (C) to GST-D3RIL3. (D) A graph of the data from A–C. Blue and red bars represent changes in lane 2 (L2) and lane 4 (L4), respectively, over lane 1 (L1). *p < 0.05 versus L1. +p < 0.05 versus L2. (E) Effects of EGTA added at different times on the CaMKIIα binding to GST-D3RIL3. EGTA was added 0, 0.5, 1, 2, or 15 min after the onset of the binding reaction. Representative immunoblots are shown above the quantified data. (F) pCaMKIIα bound to GST-D3RIL3 and the GST-D3RIL3(R210-P239) fragment. (G) Effects of six peptides derived from the R210-P239 fragment on the binding of pCaMKIIα to GST-D3RIL3(R210-P239). The first 30-amino acid sequence of D3RIL3 is shown. Bold letters (in red) indicate the potential CaMKIIα binding motif. Binding assays were performed between His-tagged WT CaMKIIα (~57 kDa), WT pCaMKIIα (~57 kDa), T286A mutant (~50 kDa), or T286D mutant (~50 kDa) proteins and immobilized GST-D3RIL3 or GST-D3RIL3(R210-P239) in the presence or absence of CaCl2 (0.5 mM), CaM (1 μM), ATP (50 μM), or EGTA (1 mM) as indicated. Bound CaMKIIα, pCaMKIIα, or mutants were visualized by immunoblots. Data are presented as means ± SEM for 4–6 experiments per group.