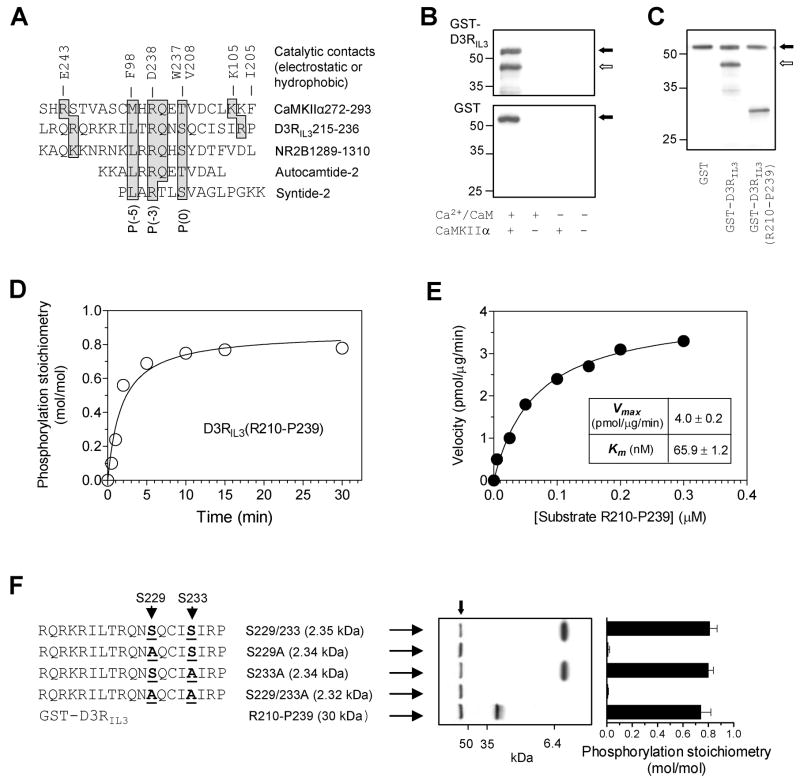
Figure 4. Phosphorylation of D3RIL3 by CaMKIIα in vitro.
(A) Alignment of CaMKII phosphorylation sequences from different substrates. The key residues shaded in gray are contacted electrostatically or hydrophobically by the residues (E243, F98, D238, W237, V208, K105, and I205) from the catalytic domain of CaMKII. (B) Autoradiographs illustrating phosphorylation of GST-D3RIL3 (upper) but not GST (lower) in the presence of Ca2+/CaM. (C) An autoradiograph illustrating phosphorylation of GST-D3RIL3 and GST-D3RIL3(R210-P239). (D) Time course of D3RIL3(R210-P239) phosphorylation. (E) Kinetic analysis of D3RIL3(R210-P239) phosphorylation. The inset table shows the kinetic parameters. (F) Phosphorylation of synthetic peptides (WT or mutants). An autoradiograph shows phosphorylation of three peptides. Phosphorylation stoichiometry (means ± SEM) was calculated from the radioactivity measured on Coomassie-stained bands by liquid scintillation counting. Substrate proteins at 0.1 μM (B, C, D, and F) or increased concentrations (E) were incubated at 30°C for 1 min (E), 10 min (B, C, and F), or indicated times (D) with [γ-32P]ATP and CaMKIIα in the presence of Ca2+ (0.5 mM)/CaM (1 μM) (C, D, E, and F) or as indicated (B). The solid arrows (B, C, and F) indicate autophosphorylated CaMKIIα whereas open arrows (B and C) indicate phosphorylated GST-D3RIL3.