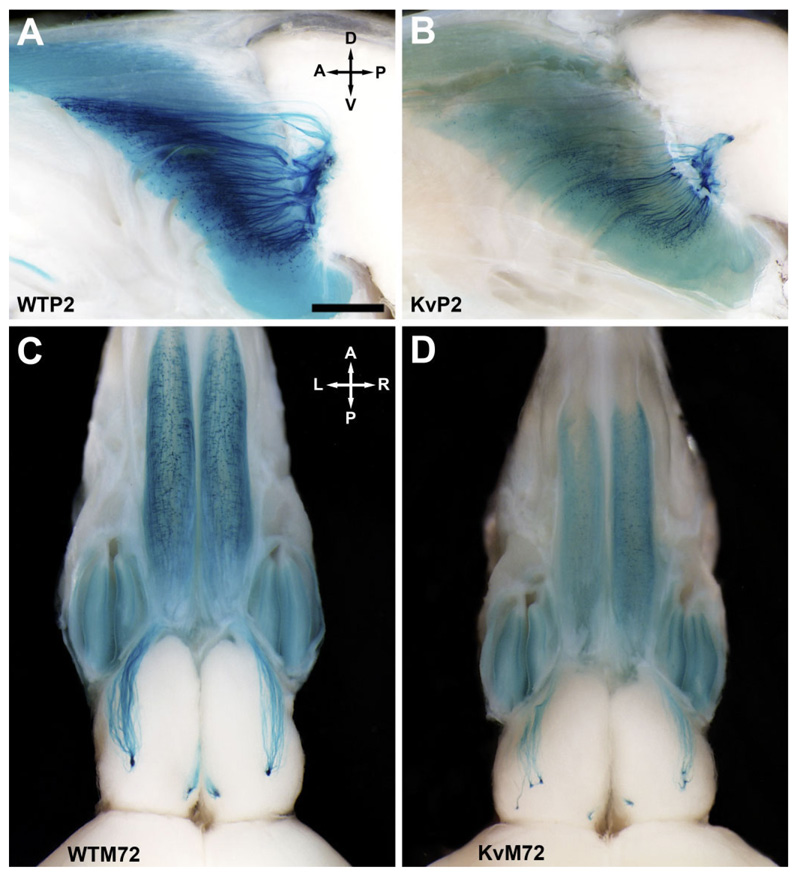
Fig. 2.
Axonal projections from P2- and M72-expressing olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) to the olfactory bulb of wild-type and Kv1.3-null mice. A: Representative whole-mount photograph of the olfactory bulb of a P2-IRES-tau-LacZ (WTP2) mouse at postnatal day 20 (P20). Axonal projections from olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) expressing the odorant receptor P2 were visualized by histological staining for β-galactosidase that was created as a fusion protein with tau immediately downstream of the P2 odorant receptor stop codon (Mombaerts et al., 1996). Brain whole-mounts were viewed through a Leica MX FLIII stereomicroscope, and images were captured with an Olympus DP10 digital camera. A, anterior; D, dorsal; P, posterior; V, ventral. B: Same as A but for a Kv1.3-null P2-IRES-tau-LacZ double-homozygous mutant mouse (KvP2). Note reduction in total β-galactosidase intensity in comparison with that of wild-type mice (A). C: Same as A but for an M72-IRES-tau-lac-LacZ (WTM72) mouse. A, anterior; L, left; P, posterior; R, right. D: Same as C but for a Kv1.3-null M72-IRES-tau-LacZ double-homozygous mutant mouse (KvM72). The glomerular projections are supernumerary, as is particularly apparent in the lateral side. Note also the moderate reduction in both olfactory bulb and epithelial size (for brain/body weight ratios, see text). Similar to that observed for KvP2 mice (B), note the reduction in total β-galactosidase intensity. Scale bar = 1 mm in A (applies to A–D).