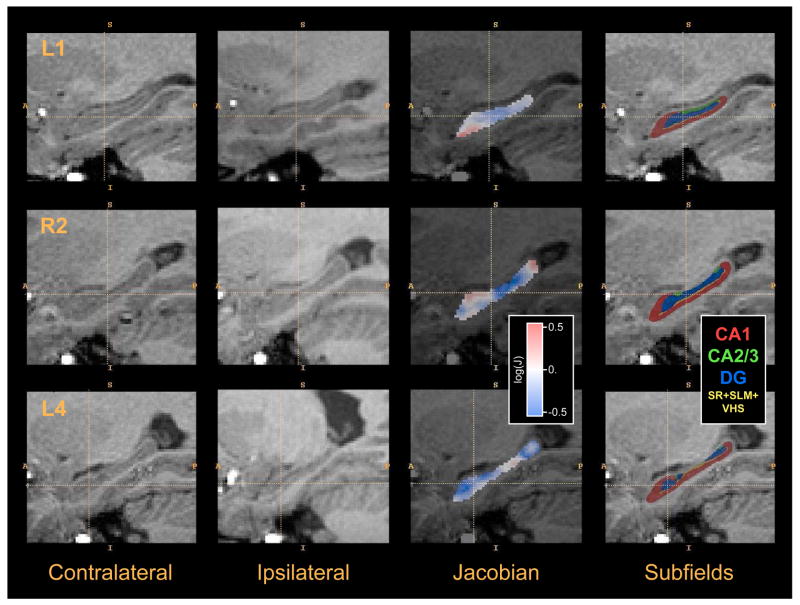
Fig. 11.
Example images from the in vivo temporal lobe epilepsy hippocampal asymmetry analysis experiment. Each row shows data from one of the subjects in the study. The first column shows a sagittal cross-section of the region surrounding the hippocampus contralateral to the seizure focus (“healthy” side). The second column shows the ipsilateral (“diseased”) hippocampus region after flipping across the midsagittal plane and rigid alignment to the healthy hippocampus. The third column plots the logarithm of the Jacobian of the transformation between the healthy hippocampus and diseased hippocampus computed by deformable image registration. Negative values (blue) indicate that a small region R in the healthy hippocampus maps to a smaller region in the diseased hippocampus; positive values (red) indicate the opposite. The Jacobian map is restricted to the the healthy hippocampus (i.e., to the manual segmentation). The last column shows the estimation of the location of hippocampal subfields in the healthy hippocampus. Subfields are mapped from the postmortem atlas using shape-based normalization.