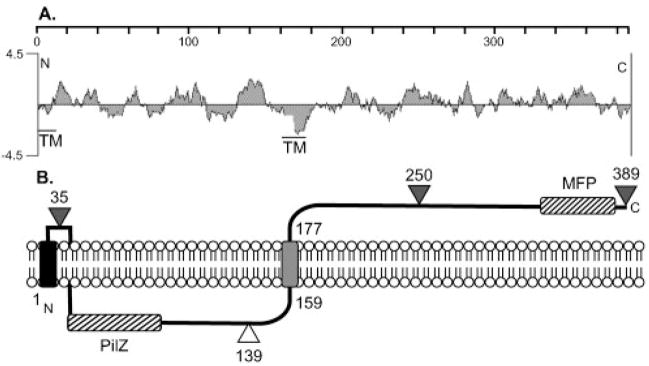
Fig. 4.
(A) A hydrophilicity plot of Alg44 and a TMpred analysis suggests a central TM domain as indicated. A putative TM is also indicated at the N terminus. The scale shows the residue numbers in Alg44. (B) Model for the orientation of Alg44 in the inner membrane based on the results of Alg44′-PhoA fusions. Triangles show the fusion joints to an in-frame PhoA, with black indicating positive activity (periplasmic) and white indicating negative activity (cytoplasmic). A TM functioning as a putative membrane anchor (e.g. uncleaved signal peptide) is indicated on the N terminus as a black rectangle in the membrane, and the grey rectangle represents the central TM domain. The locations of the PilZ domain in the cytoplasmic loop and a MFP domain in the periplasmic terminus are indicated with hatched rectangles.