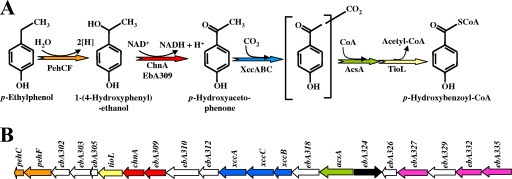
FIG. 14.
Proposed peripheral pathway for the oxidation of p-ethylphenol to 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA in Azoarcus sp. strain EbN1. (A) Enzymatic reactions of the pathway according to data described previously by Wöhlbrand et al. (379). The enzymes are indicated as follows: PehCF, putative p-ethylphenol methylhydroxylase (this enzyme was named PchCF by Wöhlbrand et al.) (379); ChnA and/or ebA309, putative 1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-ethanol dehydrogenase; XccABC, putative p-hydroxyacetophenone carboxylase; AcsA, predicted CoA synthetase; TioL, predicted thiolase. (B) Organization of the gene cluster likely involved in anaerobic p-ethylphenol oxidation in Azoarcus sp. strain EbN1 (GenBank accession number NC_006513). Genes are represented by arrows whose color codes correspond to those above (A) for the corresponding encoded enzymes. Genes of unknown function, putative p-ethylphenol/p-hydroxyacetophenone stress-related genes, and regulatory genes are indicated in white, pink, and black, respectively.