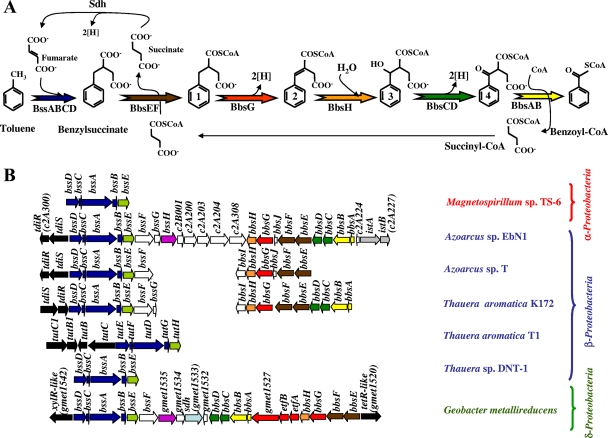
FIG. 16.
Peripheral pathway for anaerobic catabolism of toluene in bacteria. (A) Enzymatic reactions of the pathway as determined for Thauera and Azoarcus strains. The enzyme names are as follows: BssABC and BssD, subunits and activase of benzylsuccinate synthase, respectively; BbsEF, succinyl-CoA:(R)-benzylsuccinate CoA transferase; BbsG, (R)-benzylsuccinyl-CoA dehydrogenase; BbsH, putative phenylitaconyl-CoA hydratase; BbsCD, putative 2-[hydroxyl(phenyl)methyl]-succinyl-CoA dehydrogenase; BbsAB, benzoylsuccinyl-CoA thiolase; Sdh, succinate dehydrogenase. Chemical intermediates are indicated as follows: 1, (R)-benzylsuccinyl-CoA; 2, (E)-phenylitaconyl-CoA; 3, 2-[hydroxyl(phenyl)methyl]-succinyl-CoA; 4, benzoylsuccinyl-CoA. (B) Organization of the bss and bbs gene clusters in Magnetospirillum sp. strain TS-6 (GenBank accession number AB167725) (335), Azoarcus sp. strain EbN1 (accession number NC_006513) (203), Azoarcus sp. strain T (accession number AY032676) (1), T. aromatica K172 (accession numbers AJ001848 and AF173961) (155, 216), T. aromatica T1 (accession numbers U57900 and AF113168) (68, 72), Thauera sp. strain DNT-1 (accession number AB066263) (336), and G. metallireducens (accession number NC_007517) (48, 202). Genes are represented by arrows: dark blue, genes encoding benzylsuccinate synthase; brown, genes encoding succinyl-CoA:(R)-benzylsuccinate CoA transferase; red, genes encoding (R)-benzylsuccinyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bbsG) and the predicted electron acceptor system; orange, genes predicted to encode phenylitaconyl-CoA hydratase; dark green, genes predicted to encode 2-[hydroxyl(phenyl)methyl]-succinyl-CoA dehydrogenase; yellow, genes predicted to encode benzoylsuccinyl-CoA thiolase; light green, genes encoding a putative benzylsuccinate synthase chaperone; light blue, gene encoding a putative succinate-dehydrogenase flavoprotein; violet, genes encoding putative toluene transport systems, black, genes predicted to encode transcriptional regulators; gray, genes encoding a putative transposase and its helper protein; white, genes of unknown function. The 3′ end of the bssF and bssG genes from Azoarcus sp. strain T and T. aromatica K172, respectively, as well as the region between the bss and bbs clusters of these two bacteria have not been sequenced yet.