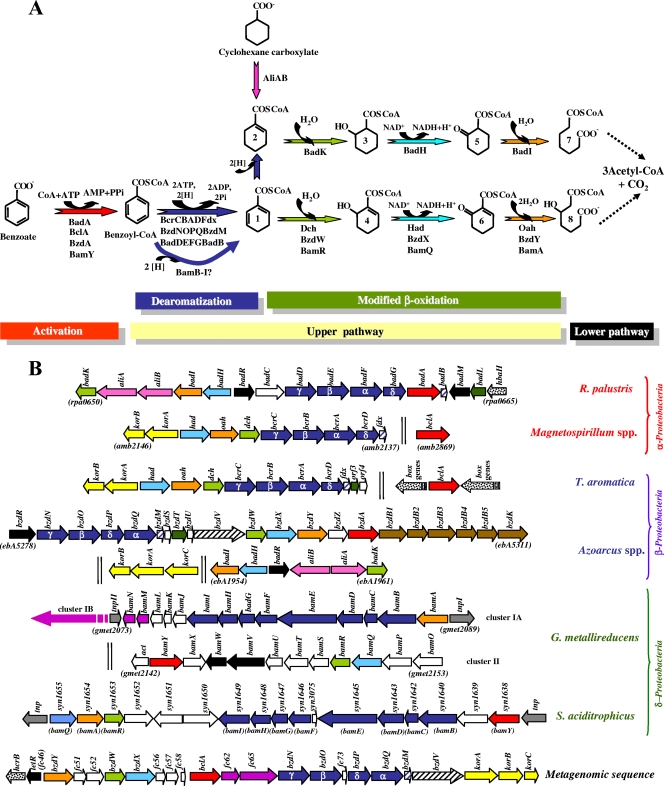
FIG. 2.
Pathway for the anaerobic catabolism of benzoate in anaerobic bacteria: the benzoyl-CoA biodegradation pathway. (A) Enzymatic reactions of the pathway. The cyclohexane carboxylate convergent pathway is also shown. The reaction steps are indicated at the bottom: I, activation of benzoate to benzoyl-CoA by benzoate-CoA ligase (red arrow); II, upper benzoyl-CoA pathway involving benzoyl-CoA dearomatization by benzoyl-CoA reductase (dark blue arrows) and modified β-oxidation via hydratation (green arrows), dehydrogenation (light blue arrows), and hydrolytic ring cleavage (orange arrows); III, lower benzoyl-CoA pathway (dotted arrows) that generates three molecules of acetyl-CoA and one CO2 (see also Fig. 3). The activation of cyclohexane carboxylate by the cognate CoA ligase (AliA) and its subsequent dehydrogenation by the cyclohexanecarboxyl-CoA dehydrogenase (AliB) are also shown (pink arrow). The metabolites are as follows: cyclohex-1,5-diene-1-carbonyl-CoA (1), cyclohex-1-ene-1-carbonyl-CoA (2), 2-hydroxycyclohexane-1-carbonyl-CoA (3), 6-hydroxycyclohex-1-ene-1-carbonyl-CoA (4), 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carbonyl-CoA (5), 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carbonyl-CoA (6), pimelyl-CoA (7), and 3-hydroxypimelyl-CoA (8). The enzymes are also indicated, and the names correspond to those of the corresponding genes. (B) Organization of the gene clusters involved in the anaerobic catabolism of benzoate in Rhodopseudomonas palustris CGA009 (GenBank accession number NC_005296), Magnetospirillum spp. (M. magneticum AMB-1 [accession number NC_007626], M. magnetotacticum MS-1 [accession number AAAP00000000], and Magnetospirillum sp. strain TS-6 [accession numbers AB167726 and AB243675]), Thauera aromatica (accession number AJ224959), Azoarcus spp. (Azoarcus sp. strain CIB [accession number AF515816], A. evansii [accession number AJ428529], and Azoarcus sp. strain EbN1 [accession number NC_006513]), Geobacter metallireducens GS-15 (accession number NC_007517), Syntrophus aciditrophicus SB (accession number NC_007759), and a metagenomic sequence (accession number CR931837). The names of the genes in the different organisms are also summarized in Table 2. Genes are represented by arrows: red, genes encoding benzoate-CoA ligases; dark blue, genes encoding the subunits of the benzoyl-CoA reductase; blue hatched, genes encoding ferredoxins associated with benzoyl-CoA reductases; yellow, KGOR-encoding genes; black hatched, genes encoding a putative NADPH:ferredoxin oxidoreductase; light green, genes encoding enoyl-CoA hydratases; light blue, genes encoding NAD-dependent hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenases; orange, genes encoding oxoacyl-CoA ring cleavage hydrolases; black, regulatory genes; dark green, genes encoding putative acyl-transferases; brown, putative transport genes; pink, genes encoding cyclohexanecarboxylate-CoA ligase (aliA) and cyclohexanecarboxyl-CoA dehydrogenase (aliB); violet, putative lower-pathway genes; dotted, genes from other aromatic catabolic pathways; gray, transposase-encoding genes; white, genes of unknown function. Two vertical lines mean that the genes are not adjacent in the genome.