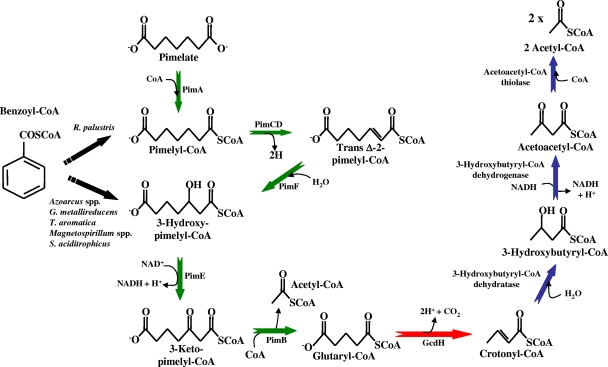
FIG. 3.
Lower benzoyl-CoA pathway. Benzoyl-CoA becomes converted into pimelyl-CoA (R. palustris) or 3-hydroxypimelyl-CoA (other bacteria) via the central benzoyl-CoA pathway (Fig. 2). Pimelate is another carbon source that funnels into this lower pathway. The C7-dicarboxyl-CoA compounds are further degraded into two molecules of acetyl-CoA and one CO2 through a series of reactions that involve a dicarboxylic acid β-oxidation pathway (green arrows), a glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase (red arrow), and a short-chain fatty acid β-oxidation pathway (blue arrows). The enzymes indicated are as follows: PimA, acyl-CoA ligase; PimCD, flavin-containing acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; PimF, enoyl-CoA hydratase; PimE, hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase; PimB, acyl-CoA acetyltransferase (β-ketothiolase); GcdH, glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase.