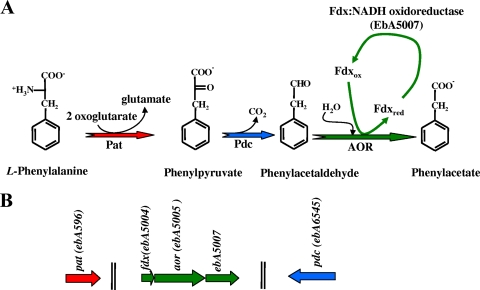
FIG. 8.
Proposed pathway for anaerobic catabolism of l-phenylalanine to phenylacetate in Thauera and Azoarcus strains. (A) Enzymatic reactions of the pathway according to data described previously by Schneider et al. (324) and Wöhlbrand et al. (378). The enzymes involved are l-phenylalanine:2-oxoglutarate transaminase (Pat), phenylpyruvate decarboxylase (Pdc), and phenylacetaldehyde oxidoreductase (AOR). Fdx (ferredoxin) and Fdx:NADH oxidoreductase are predicted to be auxiliary enzymes of AOR (378). (B) Organization of the genes likely to be involved in anaerobic catabolism of phenylalanine to phenylacetate in Azoarcus sp. strain EbN1 (GenBank accession number NC_006513). Genes are represented by arrows: red, pat gene, encoding the putative l-phenylalanine:2-oxoglutarate transaminase; blue, pdc gene, encoding the putative phenylpyruvate decarboxylase; green, genes encoding a putative phenylacetaldehyde oxidoreductase AOR and the ferredoxin and ferredoxin:NADH oxidoreductase enzymes. Two vertical lines mean that the genes are not adjacent in the genome.