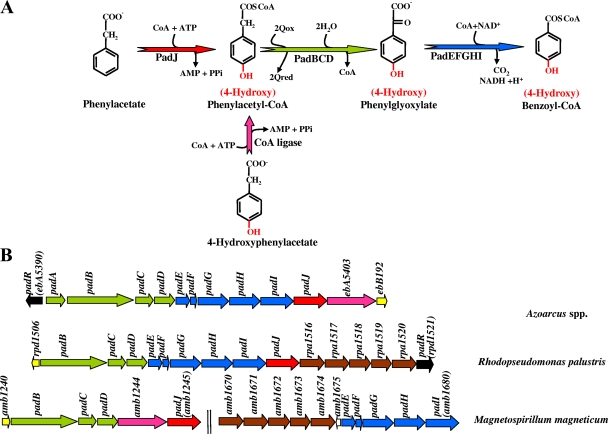
FIG. 9.
Peripheral pathway for anaerobic catabolism of (4-hydroxy)phenylacetate in bacteria. (A) Enzymatic reactions of the pathway in T. aromatica (248, 301, 324) and A. evansii (157, 248). The enzymes involved are phenylacetate-CoA ligase (PadJ), phenylacetyl-CoA:acceptor oxidoreductase (PadBCD), phenylglyoxylate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (PadEFGHI), and a proposed 4-hydroxyphenylacetate-CoA ligase (CoA ligase). (B) Organization of the gene clusters likely to be involved in anaerobic catabolism of phenylacetate in A. evansii (GenBank accession number AJ428571), Azoarcus sp. strain EbN1 (accession number NC_006513), R. palustris BisB5 (accession number NC_007958), and M. magneticum AMB-1 (accession number NC_007626). Genes are represented by arrows: red, padJ genes encoding phenylacetate-CoA ligase; pink, genes encoding a putative 4-hydroxyphenylacetate-CoA ligase; green, padBCD genes likely encoding phenylacetyl-CoA:acceptor oxidoreductase; blue, padEFGHI genes likely encoding phenylglyoxylate:NAD+ oxidoreductase; brown, genes encoding a putative ABC-type transporter; black, genes coding for putative transcriptional regulators; yellow, genes encoding a putative thioesterase; white, gene of unknown function. Two vertical lines mean that the genes are not adjacent in the chromosome.