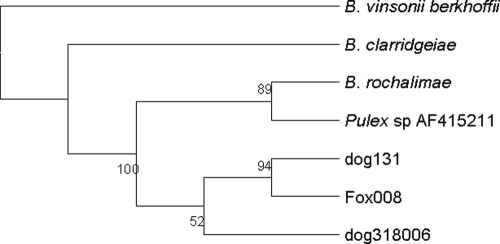
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic tree based on the 16S-to-23S intergenic spacer region showing the grouping of “B. rochalimae” strains from domestic dogs, gray foxes, a human, and a Pulex sp. flea in relation to B. clarridgeiae. The human-associated Bartonella sp. has been designated “B. rochalimae.” The tree shown is a neighbor-joining tree based on the Kimura two-parameter model of nucleotide substitution. Bootstrap values are based on 1,000 replicates. The analysis provided tree topology only, and the lengths of the vertical and horizontal lines are not significant.