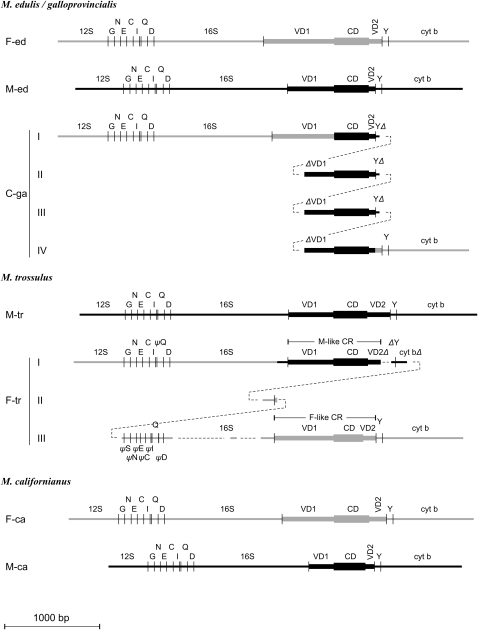
Figure 2.—
Schematic of the structure of the CR of seven genomes. Parts are aligned according to homology. F-ed, F-tr, and F-ca: the maternal genomes of M. edulis/M. galloprovincialis, M. trossulus, and M. californianus; M-ed, M-tr, and M-ca: the paternal genomes of M. edulis/M. galloprovincialis, M. trossulus, and M. californianus; C-ga: a masculinized (paternally transmitted genome) of M. galloprovincialis. Shaded lines are F-type and heavy lines are M-type sequences, respectively. 12S, 16S, cyt b: 12S-rRNA, 16S-rRNA, and Cyt b; G, N, E, C, I, Q, D, Y: the tRNAGly, tRNAAsn, tRNAGlu, tRNACys, tRNAIle, tRNAGln, tRNAAsp, and tRNATyr. VD1, CD, and VD2: the first variable, the conserved, and the second variable domains of the CR. ψ denotes a pseudogene; Δ denotes a deletion: 5′ (if it precedes) or 3′ (if it follows) the indicated gene or domain. The compound CR of two genomes, C-ga and F-tr, is given in four and three lines, respectively, to demonstrate the homology of genes or domains. Dashed lines serve to join adjacent parts. Lengths of domains are in scale.