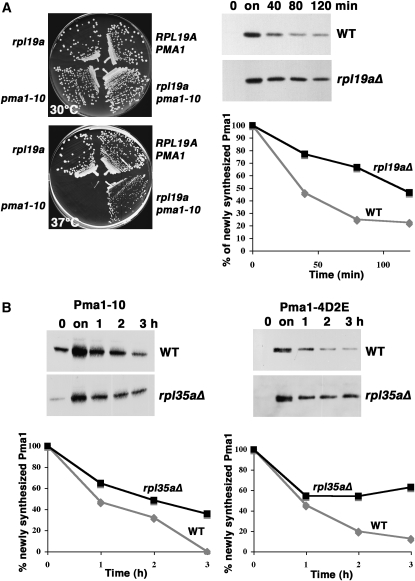
Figure 3.—
Stabilization of mutant Pma1 in the absence of ribosomal proteins Rpl19a and Rpl35a. (A) (Left panels) Suppression of temperature-sensitive growth of pma1-10 by rpl19aΔ. Strains were struck out on plates with synthetic complete medium at 30° and 37°. (Right panels) Pma1-10 stabilization. RPL19A+ (BY4741) and rpl19aΔ cells bearing pMET3-HA-pma1-10 (pKK42) were grown to midlog phase in the presence of methionine (0) and then shifted to methionine-free medium to derepress mutant Pma1 synthesis (on). Methionine was then added to repress synthesis, and cells were collected at various times of chase. Cell lysate was analyzed by Western blot with anti-HA antibody. Films were scanned and quantitated using NIH Image. (B) Mutant Pma1 stabilization in rpl35aΔ cells. HA-tagged mutant Pma1-10 (left panel) or Pma1-4D2E (right panel) were derepressed as described in A in wild-type (BY4741) and rpl35aΔ cells bearing pMET25-HA-pma1-10 (pKK7) or pMET3-HA-pma1-4D2E (pKK103). Cells were “chased” by addition of methionine. Lysate was analyzed by Western blot with anti-HA antibody. Films were scanned and quantitated using NIH Image.