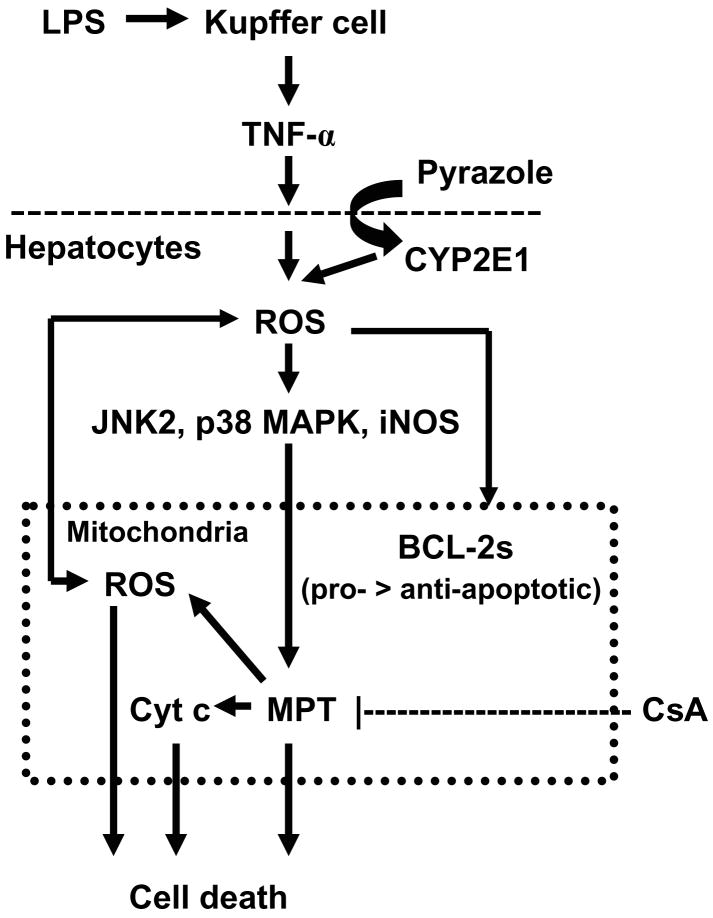
Fig. 7.
Scheme for the protection by cyclosporin A (CsA) against pyrazole plus lipopolysaccharide (LPS) liver injury. LPS induces Kupffer cells to release TNF-α, while pyrazole induces hepatocyte CYP2E1 expression. TNF-α plus CYP2E1 enhance production of ROS which can induce iNOS, and activate via phosphorylation p38 and JNK2 MAPK. Increases in ROS and reactive nitrogen species production, and activation of MAPK promotes an imbalance between anti-apoptic and pro-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins, resulting in a mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) and release of cytochrome c (Cyt c). This damage to the mitochondria increases production of ROS and causes hepatocyte necrosis. CsA prevents the MPT, blocks cytochrome c release from mitochondria, and lowers mitochondrial MDA, which protects the hepatocyte from the pyrazole plus LPS-induced necrosis.