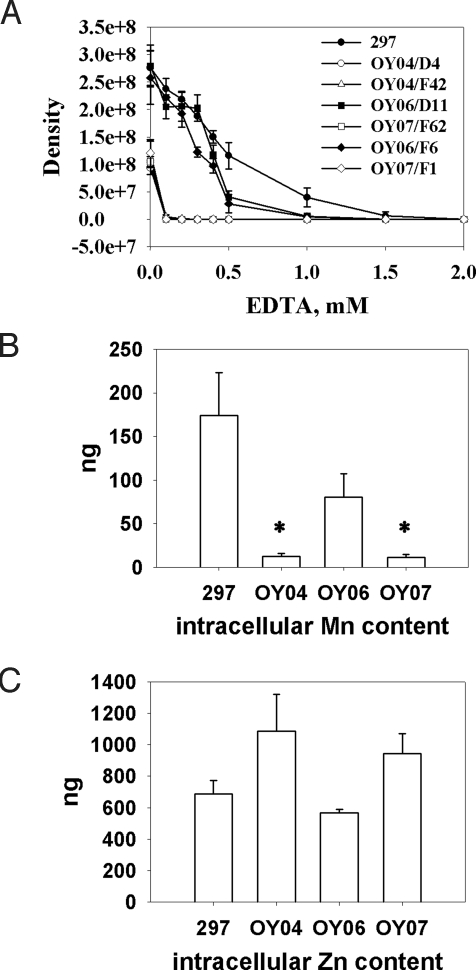
Fig. 3.
Role of metals in spirochete growth. In all experiments, BSK-II medium was inoculated with 1,000 spirochetes per mL. After growth at 37 °C for 9 days, spirochetes were collected and enumerated by darkfield microscopy. Data were derived from 3 independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations, and the asterisk indicates statistical significance using Student's t test (P < 0.05). (A) Metal ions were depleted from BSK-II medium by adding varying amounts of EDTA; bacterial growth under these conditions was monitored. (B and C) Spirochetes from 200 mL of culture were collected, and the intracellular Mn (B) and Zn (C) contents were measured by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Values are shown as nanograms per 2.5 × 1010 spirochetes of strains WT 297, bb0219 mutant OY04/D4, complemented strain OY06/D11, or mock-complemented strain OY07/F62. For Mn contents in OY04 and OY07, the detection limit (10 ng per 2.5 × 1010 spirochetes) is represented, as values were below this threshold.