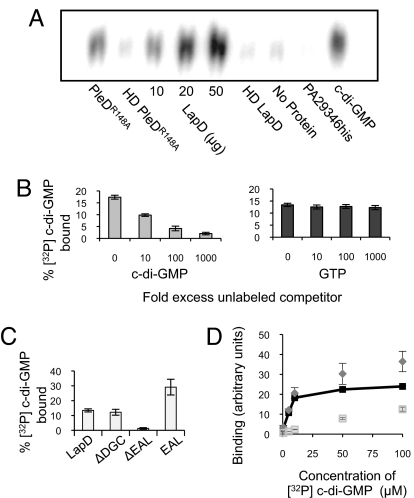
Fig. 2.
Analysis of c-di-GMP binding by LapD. (A) TLC resolution of [32P] c-di-GMP co-purified with histidine-tagged proteins. Each reaction contained 50 μg of protein unless otherwise indicated. HD = heat denatured. (B) Increasing amounts of unlabeled c-di-GMP decrease binding of LapD to [32P] c-di-GMP (Left), whereas unlabeled GTP does not compete with [32P] c-di-GMP binding at concentrations up to 1 mM (1000-fold excess) (Right). (C) c-di-GMP binding by LapD lacking the GGDEF or EAL domain or by the EAL domain alone. (D) Binding of c-di-GMP to E. coli membranes containing LapD (diamonds) or the ΔEAL protein (open squares) at increasing concentrations of ligand. Specific binding (dark squares) is binding to LapD minus binding to ΔEAL.