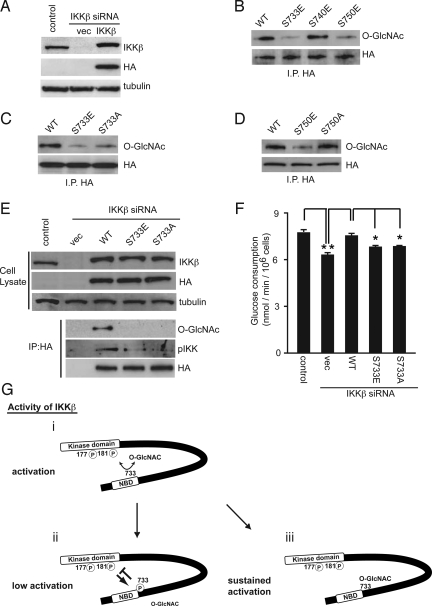
Fig. 4.
O-GlcNAcylation of IKKβ at Ser 733 regulates its catalytic activity. (A) NIH 3T3 cells infected with mouse IKKβ siRNA-expressing retrovirus were superinfected with HA-tagged human IKKβ wild type (WT). The cell extracts from the infected cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) NIH 3T3 cells infected with mouse IKKβ siRNA-expressing retrovirus were superinfected with retroviruses encoding HA-tagged human IKKβ wild type (WT), S733E, S740E, or S750E mutants. The cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti-HA antibody followed by immunoblot analysis with an anti-O-GlcNAc antibody. (C) NIH 3T3 cells infected with mouse IKKβ siRNA-expressing retrovirus were superinfected with retroviruses encoding HA-tagged human IKKβ WT, S733E, or S733A mutants. The level of IKKβ O-GlcNAcylation was examined in cells infected with each retrovirus. (D) National Institutes of Health 3T3 cells infected with mouse IKKβ siRNA-expressing retrovirus were superinfected with retroviruses encoding HA-tagged human IKKβ WT, S750E, or S750A mutants. The level of IKKβ O-GlcNAcylation was examined in the cells infected with each retrovirus. (E and F) p53−/−MEFs infected with mouse IKKβ siRNA-expressing retrovirus were superinfected with HA-tagged human IKKβ wild-type (WT), S733E, or S733A mutants. The cell extracts from the infected cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti-HA antibody followed by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies to examine the levels of IKKβ O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation at the active site of IKKα/β (E). Glucose consumption was estimated from the concentration of glucose in the culture media. Data are means ± SD. from 3 independent experiments *P < 0.01 for the indicated comparison (t test) (F). (G) A model of IKKβ activation regulated by phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation at the C-terminal domain. In the basal state, IKKβ is reciprocally modified with O-GlcNAc at Ser 733. Stimulation, such as by TNFα, induces activating phosphorylation in its kinase domain of IKKβ (i) and subsequently autophosphorylates the inactivating phosphorylation sites at its C-terminal domain, including the Ser 733 residue (ii). For IKKβ modified with O-GlcNAc, the TNFα-induced kinase activity is sustained by blockade of inactivating phosphorylation (iii).