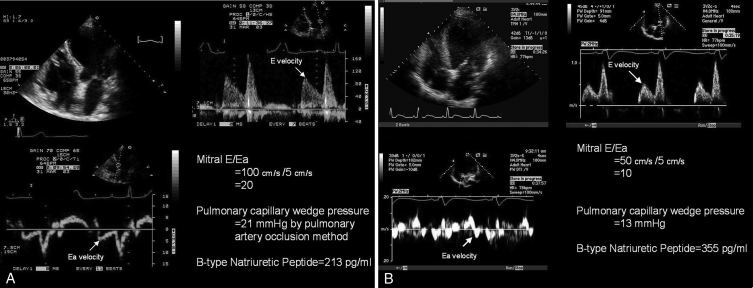
Figure 2).
A Tissue Doppler imaging in the prediction of left ventricular (LV) filling pressures: normal LV ejection fraction. This patient had an LV ejection fraction of 67% and clinical congestive heart failure. The mitral early diastolic pulsed Doppler transmitral inflow velocity to early diastolic annular velocity ratio (E/Ea) was 20, indicating elevated LV filling pressures. Simultaneous pulmonary capillary wedge pressure by Swan-Ganz catheterization was 21 mmHg. Given the elevated filling pressures, in the presence of preserved ejection fraction, the B-type natriuretic peptide level was elevated (213 pg/mL). Thus, this patient had heart failure with a normal ejection fraction. B Tissue Doppler imaging in the prediction of LV filling pressures: depressed LV ejection fraction. This patient had known depressed LV function with an ejection fraction of 29%, but did not have clinical congestive heart failure. The mitral E/Ea ratio was 10, indicating normal LV filling pressures. Simultaneous pulmonary capillary wedge pressure by Swan-Ganz catheterization was 13 mmHg. Despite the normal filling pressures, the B-type natriuretic peptide level was elevated (355 pg/mL), owing to LV dilation and depressed ejection fraction