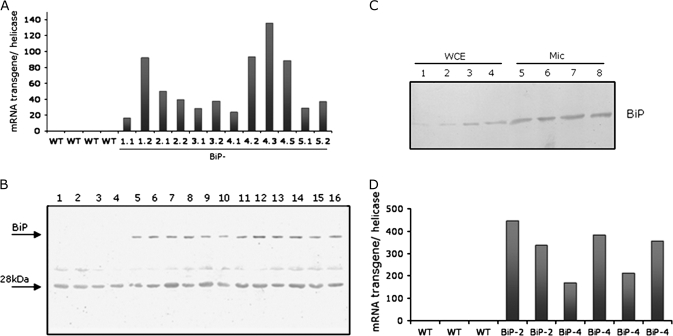
Fig. 1.
Ectopic expression of soyBiPD transgene in soybean plants. (A) mRNA abundance of soyBiPD transgene in overexpressing lines under normal growth conditions. Total RNA was isolated from leaves of wild-type (WT) plants and independently transformed soybean lines (35S:BiP-1, 35S:BiP-2, 35S:BiP-3, 35S:BiP-4, and 35S:BiP-5) and BiP transgene transcript levels were quantified by real-time PCR, using transgene-specific primers. In the nomenclature of transgenic lines, the first number indicates an independent event of transformation and the second number a different plant in a segregating population. (B) Enhanced levels of BiP in soybean transgenic lines. Equal amount of total proteins (30 μg) extracted from leaves of wild-type plants and soybean transgenic lines (as in A) were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-BiP serum. The arrows indicate the positions of BiP and a cross-reacting 28 kDa polypeptide. (C) Immunoblots of whole cell protein extracts (WCE) and microsomal fractions (Mic) of soybean leaves. Whole cell protein extracts from wild-type (lanes 1 and 2), 35S:BiP-2 (lane 3), and 35S-BiP-4 (lane 4) leaves as well as microsomal fractions from wild-type (lanes 5 and 6), 35S:BiP-2 (lane 7), and 35S-BiP-4 (lane 8) leaves were immunoblotted with anti-carboxy BiP serum. (D) Transcript accumulation of soyBiPD transgene in soybean transgenic roots. Total RNA was isolated from roots of wild-type (WT) plants and plants from two independently transformed soybean lines (BiP-2 and BiP-4) and BiP transgene transcript levels were quantified by real-time PCR, using transgene-specific primers.