Figure 4.
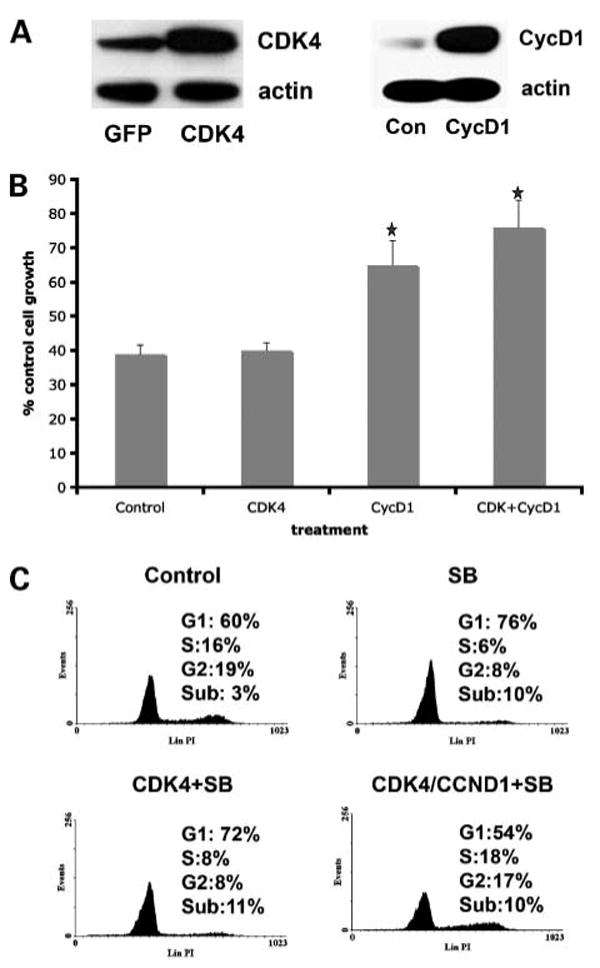
Overexpression of cyclin D1 reduces sensitivity to the BRAF inhibitor SB590885. A, infection of 451Lu melanoma cells with either virus for cyclin D1 or for CDK4. Proteins were extracted from green fluorescent protein (GFP, control), cyclin D1 (CycD1), and CDK4-infected 451Lu melanoma cells before being resolved by Western blotting. Blots were stripped and re-probed for actin to show equal protein loading. B, overexpression of cyclin D1 alone and in combination with CDK4 reduces the growth-inhibitory effect of SB590885. Cells that were infected with the green fluorescent protein virus, virus encoding for cyclin D1, virus for CDK4 or the two viruses encoding for CDK4 and cyclin D1 before being treated with SB590885 (300 nmol/L) for 72 h and analyzed using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. Data shows the mean inhibition of cell growth following drug treatment relative to untreated controls (*, P < 0.05 relative to growth inhibition in cells transfected with viral control). C, cell cycle profiles of cells treated with SB590885 that overexpress CDK4 or CDK4/cyclin D1. Cells were infected with virus as described in B before being treated with SB590885 (3 μmol/L) for 24 h. After this time, cells were fixed, harvested, and stained with propidium iodide before being analyzed by flow cytometry.
