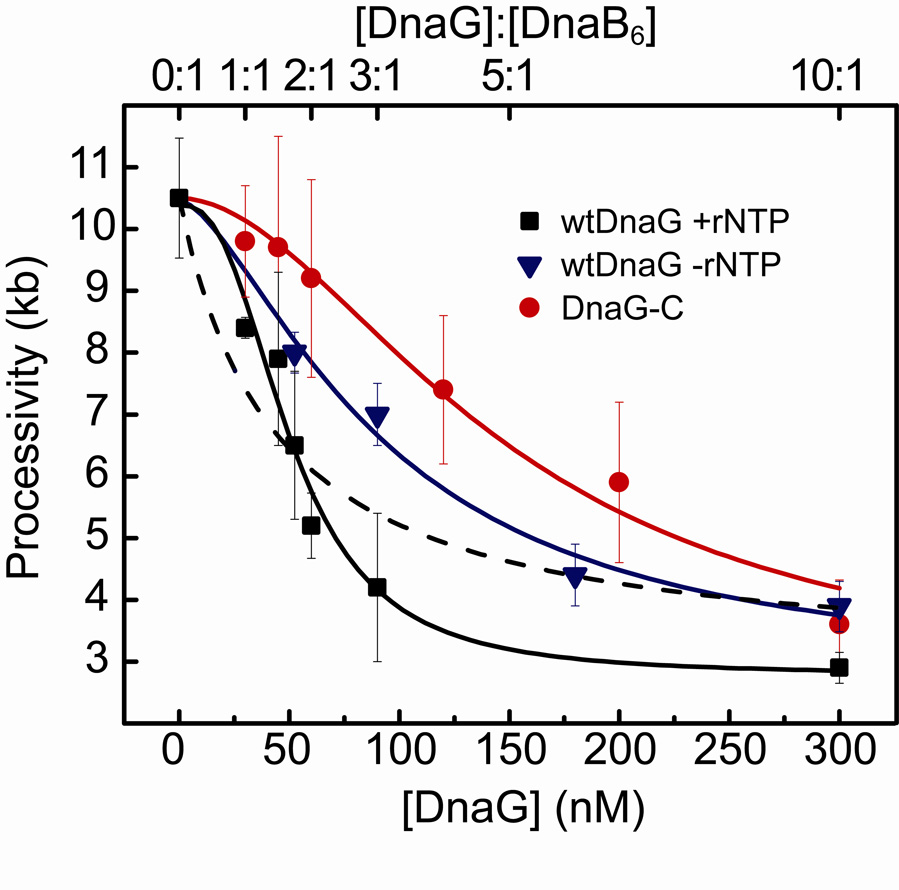
Figure 6. Cooperative DnaG-DnaB interaction is dependent upon RNA pol domain.
Cooperative DnaG-DnaB interaction is dependent upon the RNA polymerase domain of primase. Processivity values for increasing concentrations of wild-type DnaG with rNTPs (squares), of wild-type DnaG without rNTPs (triangles), and of DnaG-C without rNTPs (circles). DnaG concentration and DnaG:DnaB6 concentration ratio in solution is indicated at the bottom and top axis, respectively. Data are fit with the binding equation: , where h is the Hill coefficient, and A and B are scaling parameters. Fit lines are shown for each condition: DnaG+rNTPs (black; KD=50.7 ± 5.8 nM, h= 2.6 ± 0.8), DnaG–rNTPs (blue; KD= 93 ± 40 nM, h= 1.5 ± 0.8), and DnaG-C (red; KD= 150 ± 9 nM, h= 1.8 ± 0.2). The dashed line (blue) represents a fit to the data obtained with DnaG and rNTPs with the Hill coefficient h fixed at 1. Its poor fitting emphasizes the presence of cooperativity in DnaG-DnaB binding in the presence of ribonucleotides and RNA polymerase domains.