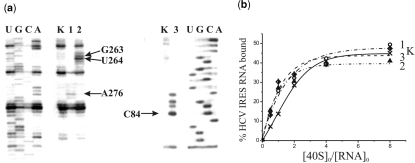
Figure 3.
Identification of sites of cross-linking of oligonucleotide derivatives to the HCV IRES by reverse transcription and binding properties of the HCV IRES derivatives. (a) Extension of [5′-32P]-labeled primers complementary to the HCV IRES sequences 331–350 (left panel) and 103–120 (right panel). Lanes 1, 2 and 3, primer extension on HCV IRES alkylated with derivatives of deoxy-oligomers complementary to the sequences 259–276, 248–267 and 62–81, respectively. Lanes K, primer extension with control HCV IRES incubated under conditions of alkylation but without oligomer derivatives. Lanes U, G, C, A, sequencing of HCV IRES. Arrows indicate positions of the reverse transcription stops caused by the cross-links. (b) Isotherms of binding of control unmodified HCV IRES (K) and its derivatives containing a perfluorophenyl azide group at A275, G263 or C83 to 40S subunits (1, 2 and 3, respectively). The initial concentration of the HCV IRES or its derivatives was 1.0 × 10−7 M. Relative error was about 10%.