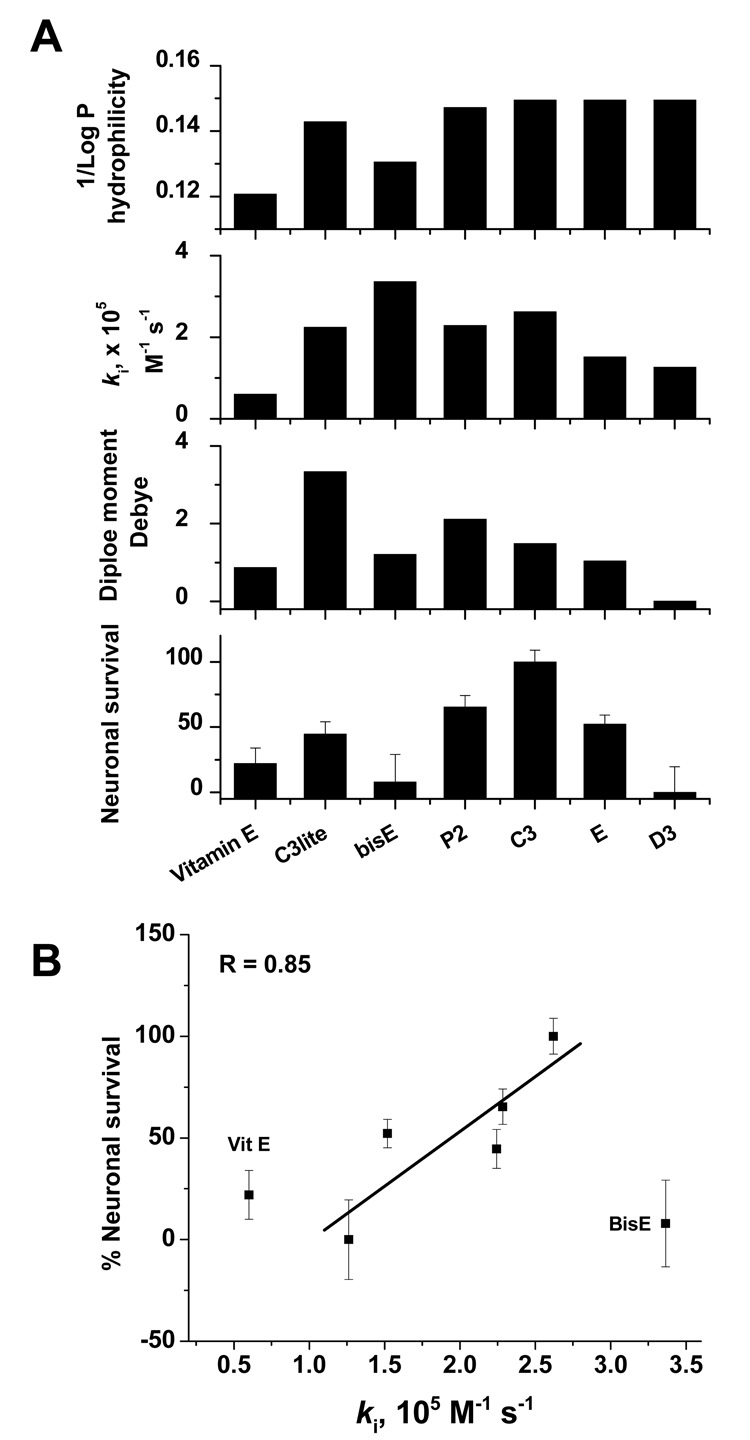
Figure 7.
Correlation between rescue from NMDA-induced neuronal death and calculated dipole moment, experimentally determined rate of superoxide elimination, and calculated hydrophilicity for each drug at 30 µM (100 µM in the case of α-tocopherol) (A). Maximum protection exhibited by the C3 isomer is consistent with it having optimal hydrophilicity, symmetry, and a high rate of superoxide elimination. Although the overall performance of each drug, including α-tocopherol, can be qualitatively explained in terms of the parameters, bisE represented an exception, since it showed the maximum ki for superoxide, but less neuroprotection than expected. Its low hydrophobicity is expected to slow its ability to enter cells, and therefore, this anomaly may reflect lack of uptake into cells during the brief (10 minute) exposure time. (B) Regression analysis indicates a good correlation (R = 0.85) between neuroprotective efficacy and ki for superoxide across isomers, with the exception of BisE, whose low aqueous solubility counterbalances it high ki. α-tocopherol is also included for comparison.