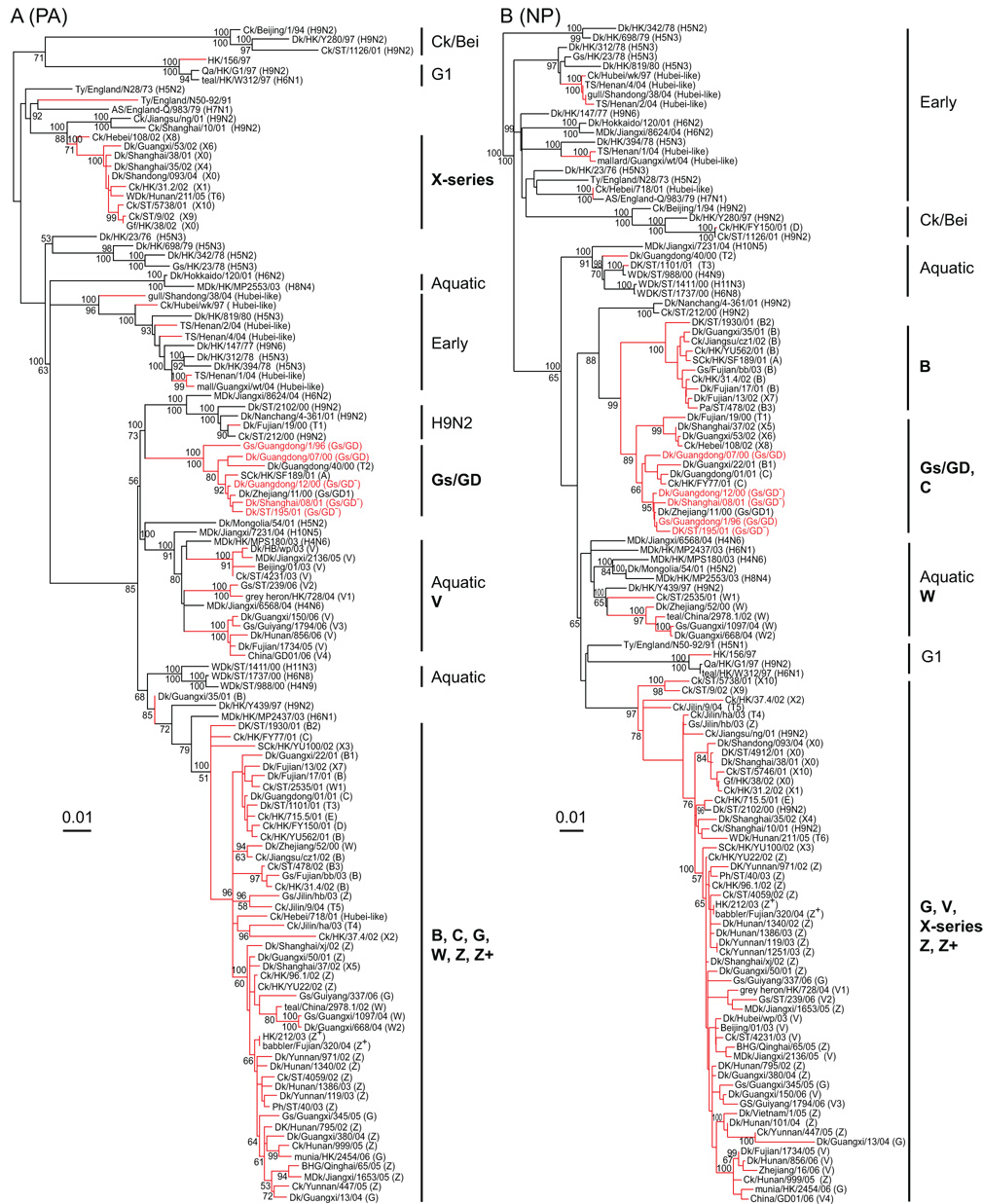
Fig. 3.
Phylogenetic relationships of polymerase acidic (PA) (A) and nucleoprotein (NP) (B) genes of representative influenza A viruses isolated in Eurasia. Analysis was based on nucleotides 1–2,148 of the PA gene and 1–1,482 of the NP gene. The PA and NP trees are rooted to equine/Prague/1/56 (H7N7). The numbers above and below the branch nodes indicate Bayesian posterior probabilities of ≥95 and neighbor-joining bootstrap values of ≥50%, respectively. Red branches indicate H5N1 viruses with H5N1 prototype virus names in red. Virus genotypes are given in parenthesis following the virus names. Major genotypes are indicated with bold text. Lineage names are provided in the Figure 2 legend. Scale bar, 0.01 substitutions per site. Abbreviation: AS, African starling; BHG, bar-headed goose; Ck, chicken; Dk, duck; Gf, Guinea fowl; Gs, goose; HK, Hong Kong; MDk, migratory duck; Pa, partridge; Ph, pheasant; Qa, Quail; SCk, silky chicken; ST, Shantou; TS, tree sparrow; Ty, Turkey; WDk, wild duck.