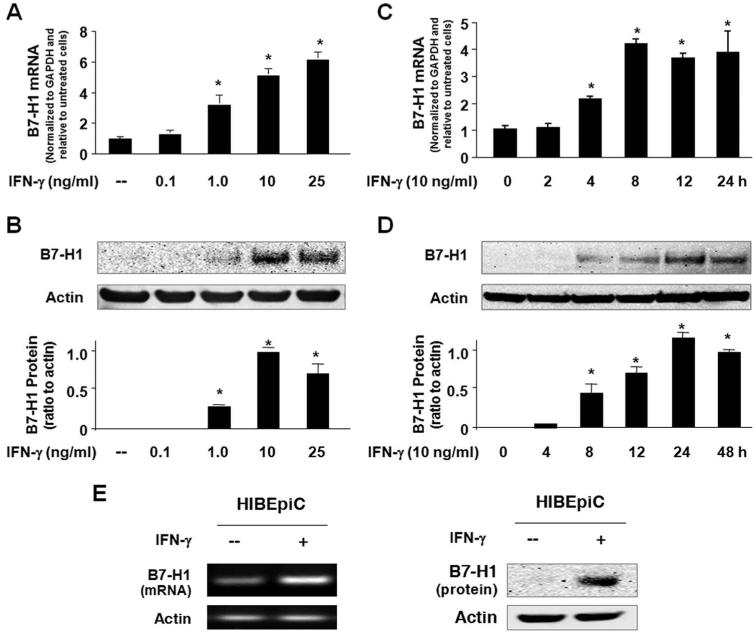
FIGURE 1.
Posttranscriptional suppression of B7-H1 exists in human cholangiocytes and IFN-γ induces cholangiocyte B7-H1 protein expression. A and B, Dose-dependent expression of B7-H1 at the message (A) and protein (B) levels in H69 cells following IFN-γ stimulation. H69 cells were exposed to culture medium with various doses of IFN-γ (0, 0.1, 1.0, 10, and 25 ng/ml) for 8 h (for real-time PCR) or 24 h (for Western blotting). A representative Western blot from three independent experiments is shown in B. Actin was blotted as a loading control. Densitometric levels of B7-H1 signals were quantified and expressed as the ratio to actin. C and D, Time-dependent expression of B7-H1 expression in H69 cells induced by IFN-γ. Cells were exposed to IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 2-48 h followed by real-time PCR (C) and Western blotting (D) for B7-H1. E, Expression of B7-H1 in HIBEpiC cells upon IFN-γ stimulation. HIBEpiC cells were exposed to culture medium with or without IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for 8 h (for RT-PCR) or 24 h (for Western blotting). *, p < 0.05, vs the nonstimulated control.