Figure 3.
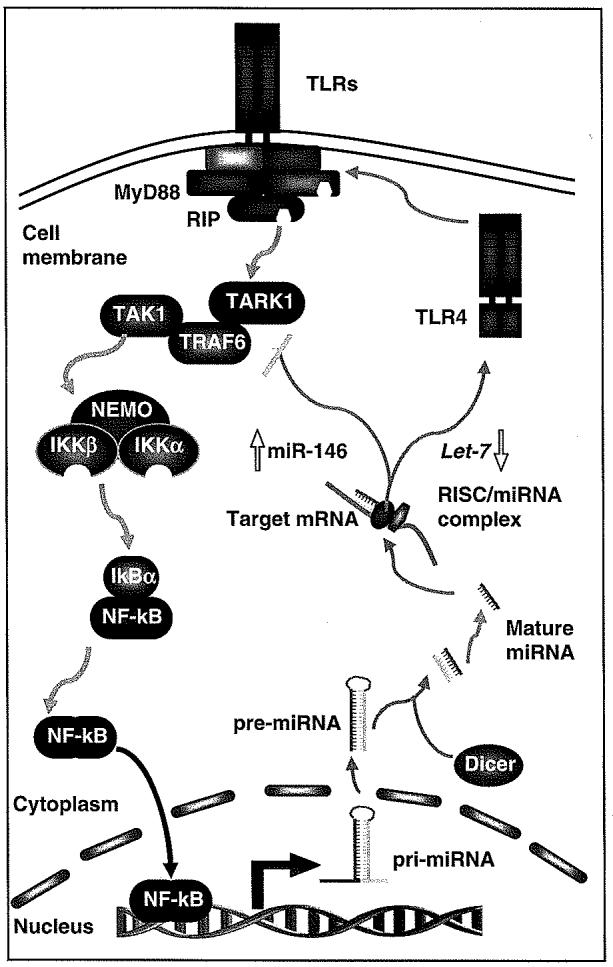
Feed-back regulation of TLR expression and activation of intracellular signaling cascades through miRNAs. Triggering of TLRs activates downstream NF-κB signaling leading to subsequent regulation of immune-response genes, including transactivation and transsuppression of miRNA genes. Primary transcripts of miRNAs are processed to form mature miRNAs, which bind to the 3′UTR of target mRNAs resulting in post-transcriptional repression. So far, miR-146 has been reported to show an increased expression upon LPS stimulation of TLR4, leading in a reduction in IRAK-1 and TRAF6 expression and attenuation of TLR4 signaling. In contrast, a downregulation of let-7 has been identified in cholangiocytes following stimulation of TLR4/NF-κB, which results in a relief of translational repression of TLR4, leading to an upregulation of TLR4 and enhancement of TLR4-associated epithelial immunity. Thus, the integration of transcriptional regulation of genes with miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation of target mRNAs results in a fine-tuned TLR-associated signaling cascades in cholangiocytes, contributing to the biliary innate immune responses to microbial infection. IκB, inhibitory protein kappaB; IKK, inhibitor of kappaB kinase; IRAK-1, IL-1R-associated kinase; miRNAs, microRNAs; NF-κB, nuclear-factor κB; RIP, receptor-interacting protein; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex; TAK, transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TRAF6, TNFR-associated factor 6; UTR, untranslated region.
