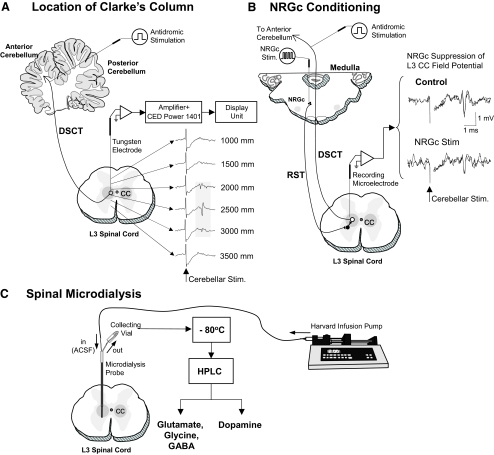
FIG. 1.
Experimental scheme illustrating procedures used for locating Clarke's column (CC) at the L3 spinal cord segment (A), optimal site for conditioning the nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis (NRGc) in the medulla oblongata (B), and sampling spinal dialysates from CC (C). The location of CC was determined by monitoring maximal amplitude field potentials evoked by stimulation of the anterior cerebellar lobule (A). Conditioning stimuli were applied to the NRGc at intensities sufficient to suppress cerebellar-evoked field potentials via the reticulospinal pathway (RST) (B). The tip of the microdialysis probe placement in CC corresponded to stereotaxic coordinates 2,500 microns ventral to where maximal cerebellar field potentials were recorded. The dialysate in each collecting vial was stored at −80°C before high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analyses (C; see methods for further details).