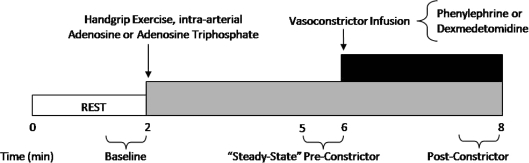
Figure 1. General experimental trial.
Each trial consisted of a 2 min baseline period. After this time period, subjects either began rhythmic handgrip exercise or received intra-arterial adenosine or adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to elevate resting forearm blood flow to levels observed during exercise. During minutes 5–6 (pre-constrictor), the doses of the α1- or α2-adrenoceptor agonists (phenylephrine or dexmedetomidine, respectively) were calculated on the basis of steady-state hyperaemic forearm blood flow and forearm volume. Subsequently, the α-agonist was infused for 2 min until minute 8. An average of forearm blood flow and mean arterial blood pressure during the final 30 s of α-agonist infusion was used to calculate the vasoconstrictor effect during all hyperaemic conditions