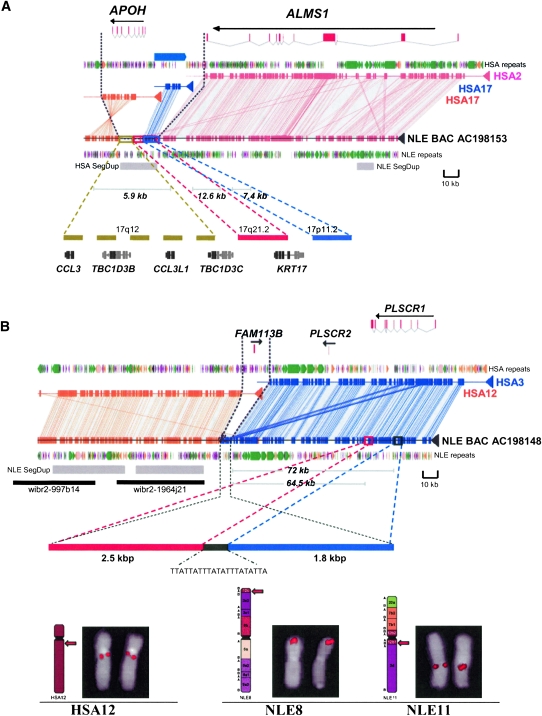
Figure 4.
Segmental duplication insertions at the breakpoints. Alignments between the NLE BAC sequences and human chromosomes are shown. These breakpoints belong to class II category. (A) Note the insertion of an ∼20 kbp segmental duplication (gray box) at the breakpoint. The sequence interval maps to several regions on human chromosome 17, some of which are depicted (solid colored bars). The length of each insertion segment, encompassing gene structures, and karyotypic mapping location are also shown. Gene fragments that do not map to the breakpoint sequences are shown in gray. (B) Insertion of a 4.3-kbp sequence at the breakpoint. Please note that the NLE gibbon BAC is in the reverse orientation. A schematic depicting the arrangement of a 4.3-kbp sequence block at the breakpoint derived from ∼2.5-kbp and 1.8-kbp blocks located ∼72 kbp and 64.5 kbp upstream, respectively, are also shown. The location of human fosmid probes (black bar), wibr2-1964j21 (chr12: 45810892–45850262) and wibr2-997b14 (chr12: 45855081–45893396), used to map the NLE-specific segmental duplication, is also shown. (Bottom panel) Representative comparative FISH signal pattern on human (HSA) and gibbon (NLE) chromosomes using a human fosmid (wibr2-1964j21) probe mapping to segmental duplications ∼8 kbp downstream from the breakpoint (see Roberto et al. [2007] for FISH methods). Both the fosmids showed signals on NLE8 (12c) and NLE11 (12b1), displaying the presence of duplications on both translocated chromosomes. Syntenic blocks between human and gibbon chromosomes are reported diagrammatically on the left side of NLE chromosomes, according to Roberto et al. (2007).