Abstract
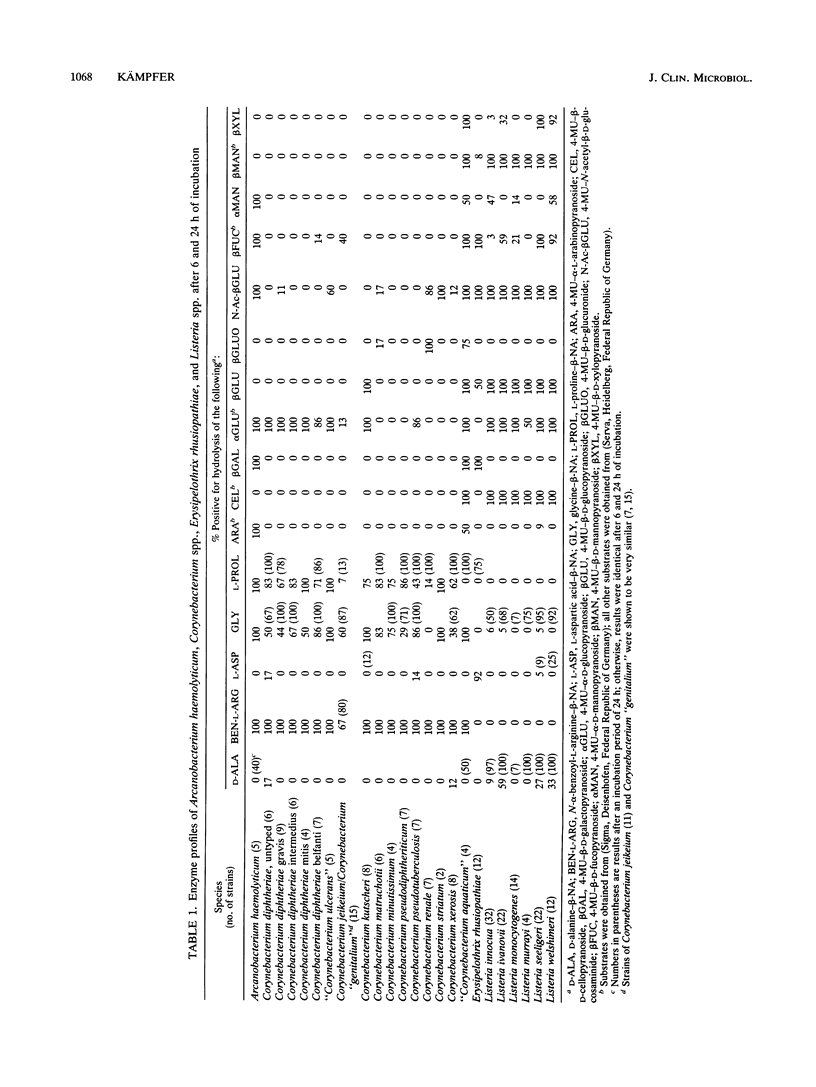
A total of 228 strains of Arcanobacterium haemolyticum, Corynebacterium spp., Erysipelothix rhusiopathiae, and Listeria spp. were investigated for their abilities to hydrolyze 60 different fluorogenic 4-methylumbelliferyl-linked and beta-naphthylamide-linked substrates within 6 and 24 h of incubation. The hydrolysis of a group of 16 fluorogenic substrates, and in particular, the glycosidase tests, in most cases showed high separation values at the genus level. When used in combination with other biochemical tests, these tests improved the differentiation of coryneform bacteria and phenotypically similar organisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Athalye M., Noble W. C., Minnikin D. E. Analysis of cellular fatty acids by gas chromatography as a tool in the identification of medically important coryneform bacteria. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 May;58(5):507–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayston R., Higgins J. Biochemical and cultural characteristics of "JK" coryneforms. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jun;39(6):654–660. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.6.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. D., Jones D., Schofield G. M. Reclassification of 'Corynebacterium haemolyticum' (MacLean, Liebow & Rosenberg) in the genus Arcanobacterium gen.nov. as Arcanobacterium haemolyticum nom.rev., comb.nov. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jun;128(6):1279–1281. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-6-1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista A. T., Coppola K. M., Furness G. Relationship between group JK corynebacteria and the biotypes of Corynebacterium genitalium and Corynebacterium pseudogenitalium. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Aug;30(8):1052–1057. doi: 10.1139/m84-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Peterkin P. I. Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):476–511. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.476-511.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freney J., Duperron M. T., Courtier C., Hansen W., Allard F., Boeufgras J. M., Monget D., Fleurette J. Evaluation of API Coryne in comparison with conventional methods for identifying coryneform bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):38–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.38-41.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasmick A. E., Bruckner D. A. Comparison of rapid identification method and conventional substrates for identification of Corynebacterium group JK isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1111–1112. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1111-1112.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. C., Smith I. D., Anstey R. J., Thornley J. H., Rennie R. P. Rapid identification of antibiotic-resistant corynebacteria with the API 20S system. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):245–247. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.245-247.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämpfer P., Böttcher S., Dott W., Rüden H. Physiological characterization and identification of Listeria species. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1991 Oct;275(4):423–435. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80164-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämpfer P., Rauhoff O., Dott W. Glycosidase profiles of members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2877–2879. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2877-2879.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky B. A., Goldberger A. C., Tompkins L. S., Plorde J. J. Infections caused by nondiphtheria corynebacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):1220–1235. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.6.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lämmler C., Blobel H. Comparative studies on Actinomyces pyogenes and Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1988;177(2):109–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00189532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manafi M., Kneifel W., Bascomb S. Fluorogenic and chromogenic substrates used in bacterial diagnostics. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):335–348. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.335-348.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. J., Johnson E. Corynebacteria: incidence among samples submitted to a clinical laboratory for culture. Med Lab Sci. 1990 Jan;47(1):36–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maximescu P., Oprişan A., Pop A., Potorac E. Further studies on Corynebacterium species capable of producing diphtheria toxin (C. diphtheriae, C. ulcerans, C. ovis). J Gen Microbiol. 1974 May;82(1):49–56. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlin J. Listeria monocytogenes, recent advances in the taxonomy and epidemiology of listeriosis in humans. J Appl Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;63(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1987.tb02411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. R., Tillotson G. S. Identification of Actinomyces (Corynebacterium) pyogenes with the API 20 Strep system. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1865–1866. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1865-1866.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocourt J., Catimel B. Caractérisation biochimique des espèces du genre Listeria. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Oct;260(2):221–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slifkin M., Gil G. M., Engwall C. Rapid identification of group JK and other corynebacteria with the Minitek system. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):177–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.177-180.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneath P. H., Johnson R. The influence on numerical taxonomic similarities of errors in microbiological tests. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):377–392. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Graevenitz A., Osterhout G., Dick J. Grouping of some clinically relevant gram-positive rods by automated fatty acid analysis. Diagnostic implications. APMIS. 1991 Feb;99(2):147–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1991.tb05132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


