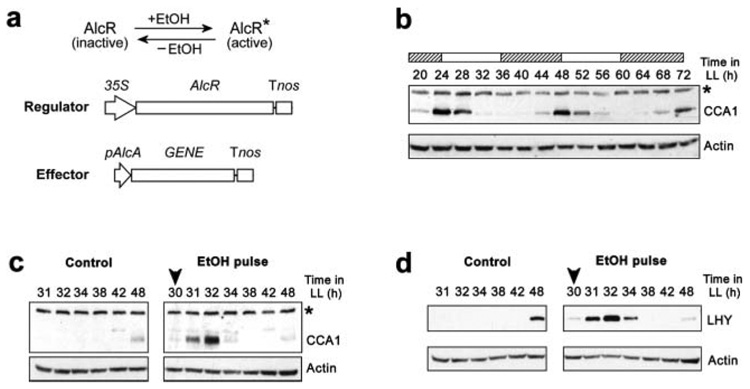
Figure 1. Ethanol (EtOH)-mediated pulses of CCA1 and LHY expression in plants.
(a) DNA constructs for the EtOH-inducible system. The ability of AlcR to function as a transcriptional activator is dependent on the presence of EtOH. Active AlcR binds the inducible promoter, pAlcA, and promotes transcription of the gene-of-interest. Tnos = terminator of the NOS gene; 35S = constitutive promoter. (b) Western blot showing the rhythm of CCA1 abundance in WT plants under continuous light (LL). (c, d) Western blots showing pulses of protein following an EtOH vapor treatment at 30 h in LL. (c) Pulse of CCA1 protein in Alc∷CCA1 seedlings. (d) Pulse of LHY protein in Alc∷LHY seedlings. Treatment time is marked by the arrowhead. Control plants were not treated. Asterisk = nonspecific band. Subjective day and subjective night are denoted by white and hatched bars, respectively.