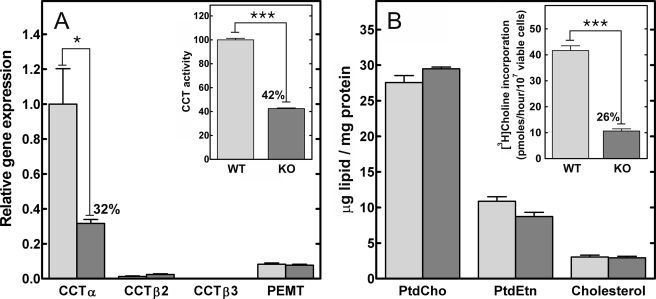
FIGURE 2.
Real time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR, CCT activity, and lipid content of WT and KO splenic B-cells. Splenic CD19-positive B-cells were isolated by positive selection from wild-type (light gray) and KO (dark gray) mice. A, Pcyt1a (CCTα), Pcyt1b (CCTβ2 or CCTβ3 transcripts), and Pemt (phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase) mRNA levels were measured by real time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. The amount of each mRNA was normalized to the level of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA and then to Pcyt1a expression in the WT B-cell population. A (inset), total cellular CCT specific activity was measured in lysates of WT and KO B-cells. The specific activity in the wild-type B-cells was 1.75 ± 0.04 nmol/min/mg (n = 4). B, total lipids were extracted from the purified WT and KO B-cells, and the amount of PtdCho, phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn), and cholesterol were quantified and normalized to protein content. B (inset), WT and KO B-cells were metabolically labeled with [3H]choline to compare the rates of PtdCho synthesis. The data are the mean ± S.E. from at least three independent determinations in two independent experiments.