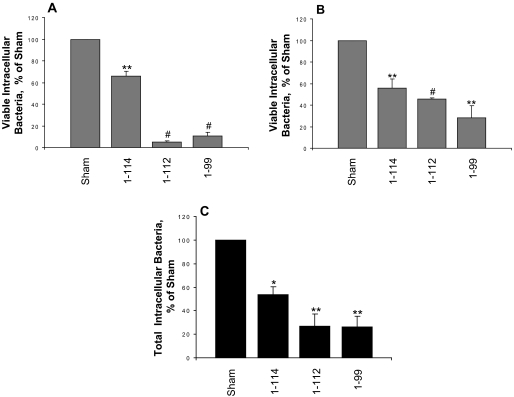
FIGURE 5.
C-terminal deletion of S100A9 increases resistance to Listeria and Salmonella invasion. KB-sham, KB-S100A8/A91–114, KB-S100A8/A91–112, and KB-S100A8/A91–99 were analyzed for bacterial invasion using an antibiotic protection assay as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Monolayers were incubated with L. monocytogenes ATCC 10403S (A) or S. typhimurium ATCC 14028 (B) at an m.o.i. of 100:1 and 1:1, respectively, for 2 h. Each experiment was performed in triplicate wells. Values are means ± S.E. of viable intracellular bacteria, relative to KB-sham (100%) from at least three independent experiments. C, immunofluorescence staining for intracellular and extracellular Listeria in KB-sham, KB-S100A8/A91–114, KB-S100A8/A91–112, and KB-S100A8/A91–99 transfectants. Monolayers were incubated with L. monocytogenes for 2 h. The intracellular bacteria were enumerated and reported as means ± S.E. relative to KB-sham (100%). The results shown are from three independent experiments (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; #, p < 0.001).