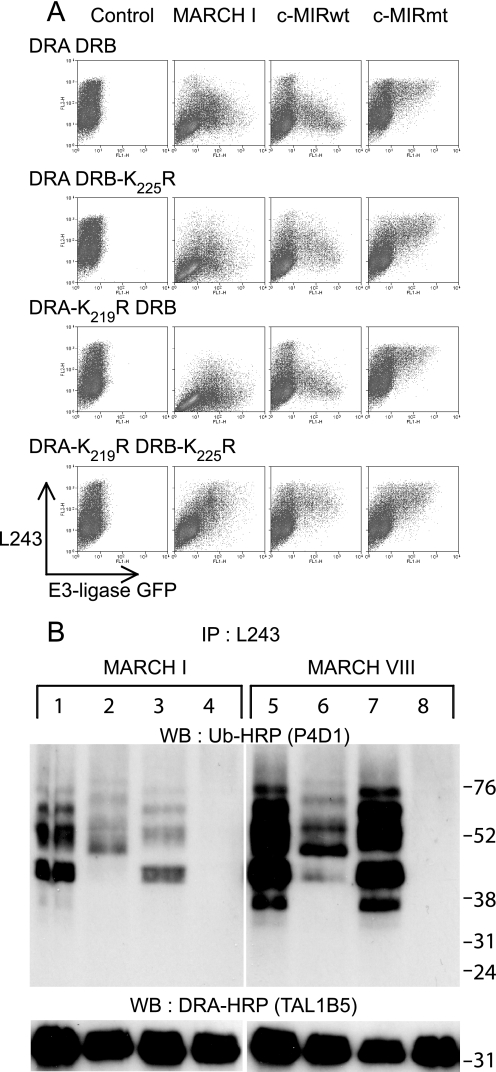
FIGURE 3.
Lysine residues Lys219 and Lys225 on HLA-DRα and HLA-DRβ, respectively, are subject to polyubiquitination. A, 293T cells were transiently co-transfected with wild-type or mutated forms of HLA-DRα and HLA-DRβ, together with either MARCH I, c-MIRwt, or c-MIRmt. The levels of surface HLA-DR were assessed by FACS using PE-L243 in the FL2 channel. E3 ligase expression was monitored indirectly by measuring GFP expression in the FL1 channel. All combinations of DRα and DRβ resulted in MARCH I- and c-MIRwt (MARCH VIII)-induced DR down-regulation, except for DRA-K219R/DRB-K225R. No change in surface HLA-DR expression was seen in the presence of c-MIRmt. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. B, HLA-DR was immunoprecipitated (IP) from lysates of the transfected cells depicted above using L243 monoclonal antibody directly conjugated to Sepharose. After standard SDS-PAGE separation and Western transfer (WB), DRα was detected with HRP-TAL1B5, and ubiquitinated HLA-DR was detected with the anti-ubiquitin antibody HRP-P4D1. Lanes 1–4 were transfected with MARCH I; lanes 5–8 were transfected with MARCH VIII. Lanes 1 and 5 expressed DRA and DRB; lanes 2 and 6 expressed DRA and DRB-K225R; lanes 3 and 7 expressed DRA-K219R and DRB; and lanes 4 and 8 expressed DRA-K219R and DRB-K225R. The upper panels show ubiquitinated HLA-DR, as detected with HRP-P4D1, the lower panels show DRα as detected by HRP-TAL1B5. No additional bands suggestive of ubiquitinated DRα were evident in the lower panels, even after long exposure. The upper panel shows that both DRα and DRβ are subject to polyubiquitination. The signal for DRβ is stronger than for DRα. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.