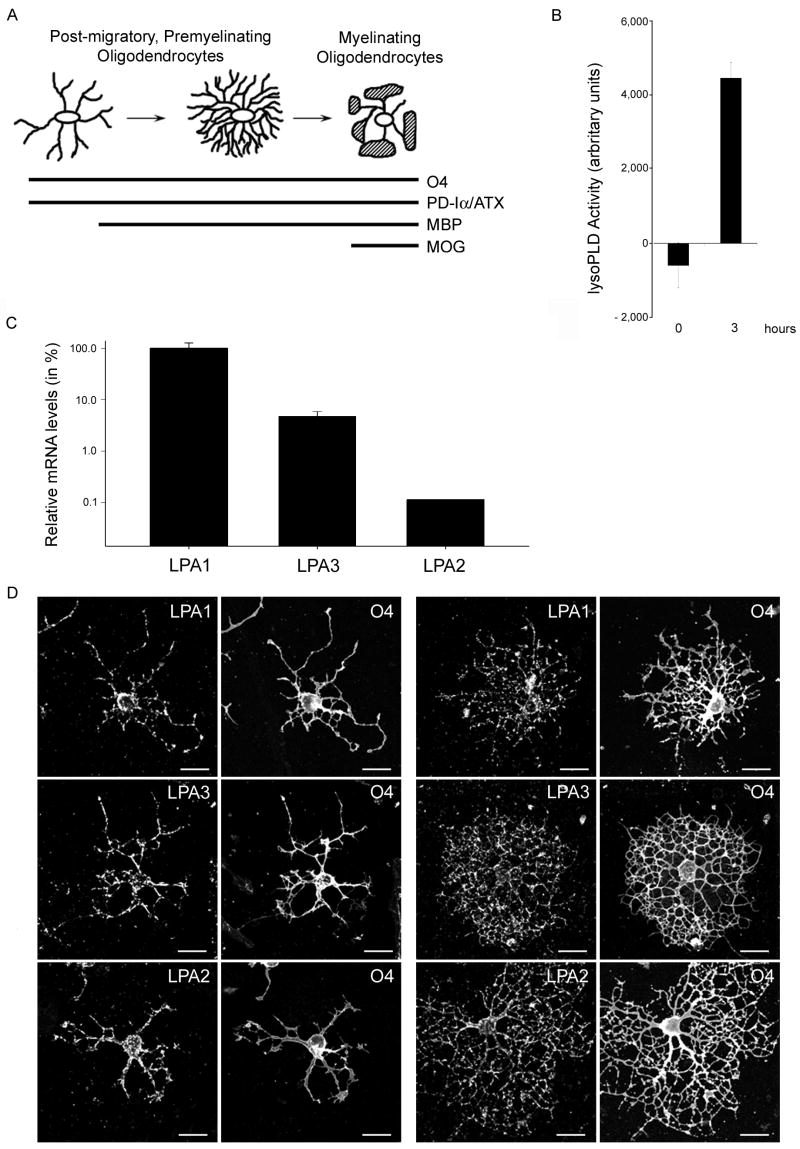
Fig. 1.
Differentiating oligodendrocytes secrete enzymatically active PD-Iα/ATX and express all three classical LPA receptors. A. Scheme of morphological and gene expression characteristics of differentiating oligodendrocytes. At all stages oligodendrocytes express the cell surface antigen O4 and the secreted protein phosphodiesterase-Iα/autotaxin (PD-Iα/ATX). The myelin proteins myelin basic protein (MBP) and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) are expressed with increasing stages of maturation. B. PD-Iα/ATX’s lysoPLD activity was determined in tissue culture supernatants from O4 immunopanned oligodendrocytes (4 days after plating) using the fluorogenic assay described by Ferguson et al. (2006). Means ± SEM of three independent experiments done in triplicates are shown. Numbers on the Y-axis represent fluorescence increase as a measure for lysoPLD activity in arbitrary units. C. Relative LPA receptor mRNA levels present in differentiating oligodendrocytes. mRNA levels were determined by real-time qRT-PCR [40] and are presented in % on a logarithmic scale. LPA1 mRNA levels were set to 100% and the levels for LPA3 and LPA2 calculated accordingly. Means ± SEM of three pooled samples run in triplicate are shown. D. Immunocytochemistry of differentiating oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrocytes were isolated by O4 immunopanning and double-immunostained 4 days after plating for the O4 antigen and for LPA1, 2 or 3. Scale Bar: 20 μm.