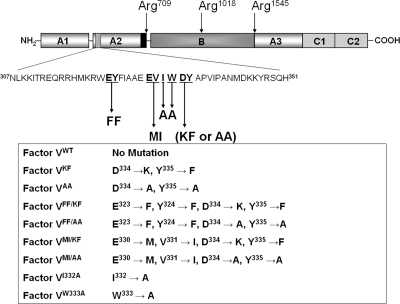
Figure 1.
Proteolytic processing of human factor V. Factor V is composed of 2196 amino acids and has three A domains (A1, A2, and A3), a connecting B region, and two C domains (C1 and C2). The procofactor is activated following three cleavages by thrombin at Arg709, Arg1018, and Arg1545. The latter cleavage is the last to occur and is a prerequisite for light chain formation and maximum cofactor activity generation. These cleavages release the active cofactor composed of heavy and light chains associated in the presence of divalent metal ions, and two activation fragments. The mutations within a 45-amino acid region of the A2 domain of the heavy chain of the molecule that is involved in cofactor activity (hatched box) are indicated together with the designation for the recombinant mutant factor V molecules created and used throughout the paper. The black box preceding cleavage at Arg709 depicts the acidic COOH-terminal region of factor Va that is essential for optimum cofactor activity.