Fig. (7).
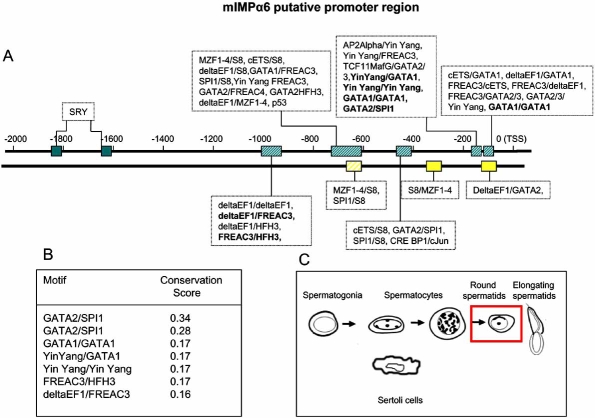
Figs. (5-7).Identification of paired transcription factor binding sites that are likely to be functional in the putative promoter regions of mouse IMP αs.A representative member of each IMP α subfamily is given (IMP α2, 3 and 6). Promoter modules 0 to +1κB upstream of the transcriptional start sites (TSS) were identified using the K-SPMM database – a TRANSFAC based, spermatogenesis-specific database. Additional modules (up to +2κB from the TSS) were identified beyond the 1-kB limit of the KSPMM analysis by a TRANSFAC based promoter search not restricted to germ cells (Figs. 4-6A). Those modules displaying particularly high per-base conservation between 4 different eukaryotic species (M. musculus, H. Sapiens, C. Familiaris, R. Norvegicus and G. Gallus) are highlighted in bold, and listed with their conservation scores (Figs. 4-6B). The testicular cell types that express other genes with the same promoter motifs (identified via K-SPMM) of the given IMP α, are highlighted in Figs. (5-7C). i.e. elongating spermatids do not express mRNAs from genes that possess the motifs detected for importin α2, whereas each of the motifs have been detected in the mRNAs from genes in each of the other testicular cell types.