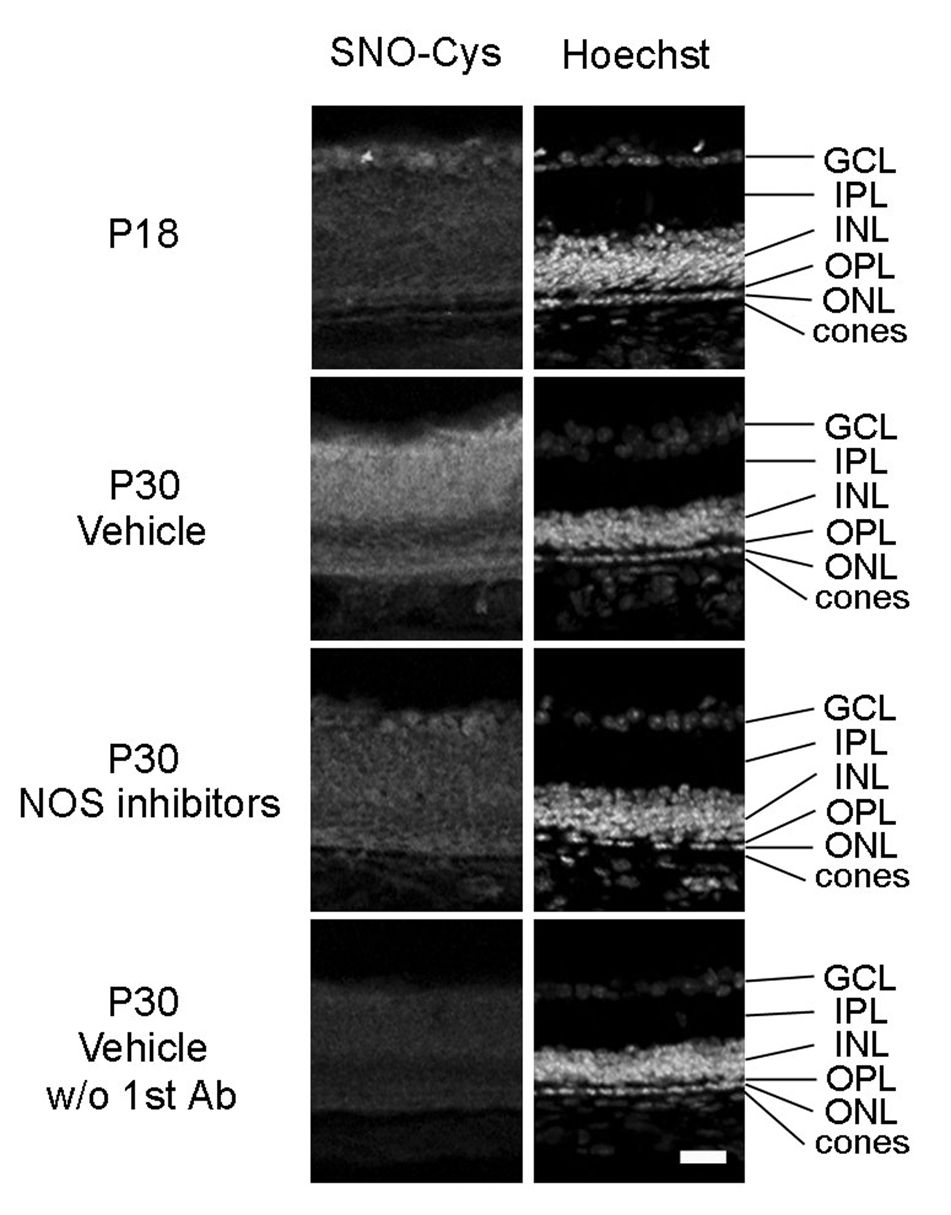
Figure 1. A mixture of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitors prevents S-nitrosylation of cysteine thiols in proteins in the retinas of rd1 mice.
Between postnatal day (P) 18 and P30, rd 1 mice were given twice daily intraperitoneal injections of vehicle or vehicle containing a mixture of four NOS inhibitors, L-NNA, L-NAME, L-NMMA, and aminoguanidine. Ocular sections were stained for S-nitrosocysteine (SNO-Cys, column 1) and Hoechst, which stains all cell nuclei (column 2). In rd1 mouse retina, there was minimal staining for SNO-Cys at P18 (column 1) that was substantially increased in P30 vehicle-treated mice throughout the entire retina including the area of remaining photoreceptors (column 2). This increase was blunted by treatment with NOS inhibitors (column 3). In the absence of primary antibody, there was essentially no staining in the retinas of P30 vehicle-treated mice. Results were identical in 2 mice for each time point/condition. Scale bar = 50 µm