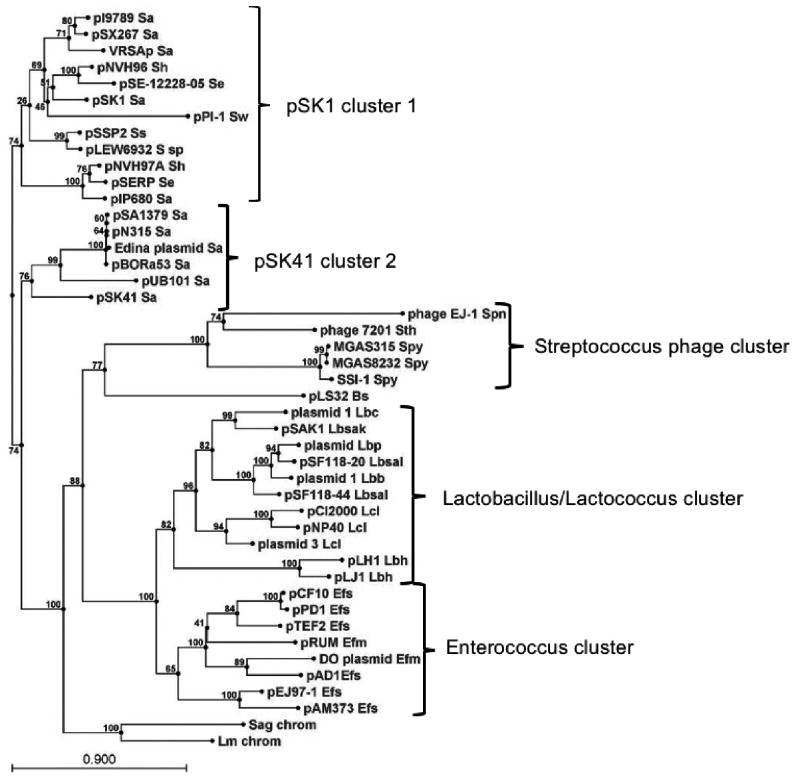
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of RepA homologs. The RepA homologs were retrieved from the NCBI database by a standard BLAST search using pAD1 RepA as query. The tree was drawn using the CLC Combined Workbench sequence analysis software at default settings; bootstrap values are indicated at nodes. Clusters described in the text are bracketed and labeled with the associated genera. The following species abbreviations are used: Bs, Bacillus subtilis; Efm, Enterococcus faecium; Efs, Enterococcus faecalis; Lbb, Lactobacillus brevis; Lbc, Lactobacillus casei; Lbh, Lactobacillus helveticus; Lbp, Lactobacillus paracasei; Lbsak, Lactobacillus sakei; Lbsal, Lactobacillus salivarius; Lcl, Lactococcus lactis; Lm chrom, Leuconostoc mesenteroides chromosomal locus; Sa, Staphylococcus aureus; Se, Staphylococcus epidermidis; Sag chrom, Streptococcus agalactiae chromosomal locus; Sh, Staphylococcus haemolyticus; Spn, Streptococcus pneumoniae; Spy, Streptococcus pyogenes; Ss, Staphylococcus saprophyticus; S sp, undefined Staphylococcus species strain 693-2; Sth, Streptococcus thermophilus; Sw, Staphylococcus warneri. The references and accession numbers for these sequences are provided in Table 1.