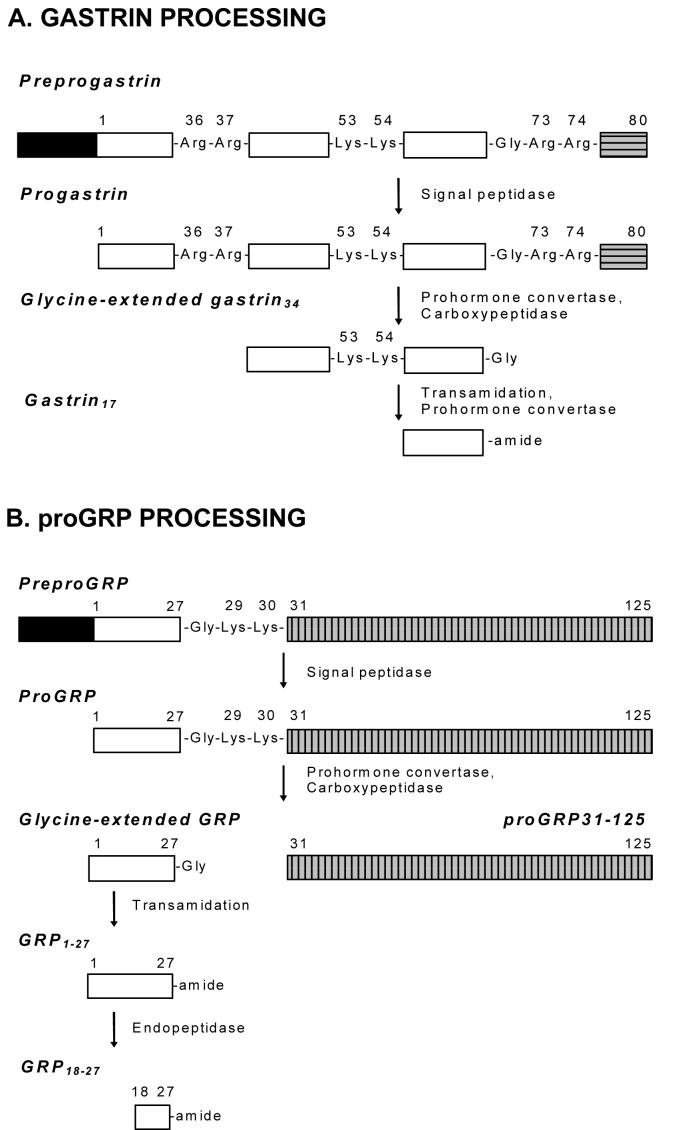
Figure 1. Processing of progastrin and proGRP.
Preprogastrin (A, 101 amino acids) and preproGRP (B, 148 amino acids) are converted to progastrin (80 amino acids) and proGRP (125 amino acids), respectively, by removal of their signal peptides (black boxes). The sequential action of prohormone convertases and carboxypeptidase E then converts the prohormones to glycine-extended forms. The extent of conversion of glycine-extended to amidated forms by the amidation enzyme PAM is dependent on the tissue. Both the prohormones and amidated forms are independently active via different receptors. Fragments from the C-terminal region of progastrin (CTFP, horizontally hatched gray box) and proGRP (proGRP31-125, vertically hatched gray box) are also biologically active, and activity is again mediated by different receptors from the corresponding amidated hormones.