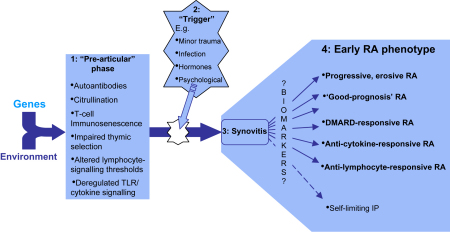
Fig. 2.
Various pathogenetic pathways account for the heterogeneity of the early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) phenotype. During both the pre-articular phase (1) and the triggering of synovitis itself (2), genetic and environmental determinants together induce a combination of pathogenetic pathways whose common outcome is a syndrome of synovitis ultimately recognizable as RA (3). The relative contributions of the various pathways in turn define an individual's disease phenotype (4). It is hoped that the search for biomarkers will yield a means of stratifying early RA into prognostically and therapeutically relevant subsets. TLR, ‘Toll-like’ receptor; DMARD, disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug; IP, inflammatory polyarthritis.