Figure 1.
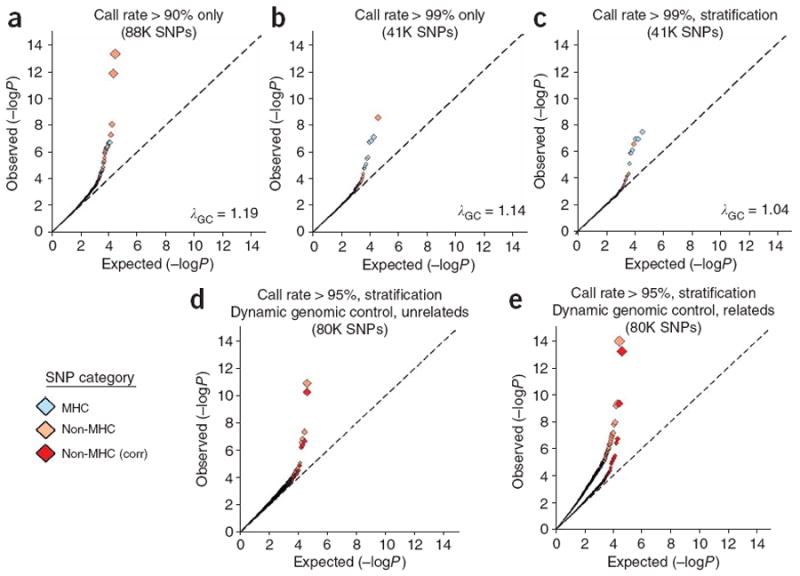
Q-Q plots of GWA analyses in unrelated individuals: influence of missing genotype data and population stratification. We conducted GWA analysis of BRASS rheumatoid arthritis cases compared to unrelated FHS controls. Light blue diamonds indicate SNPs within the extended MHC region (defined as chromosome 6, 25–35 Mb), pink diamonds indicate non-MHC SNPs and red diamonds indicate non-MHC SNPs following correction by dynamic genomic control (corr). (a,b) 88,000 (88K) SNP panel (a; >90% call rate) and 41K SNP panel (b; >99% call rate) with no attempt to correct for population stratification. P values were generated by 2 × 2 contingency tables of allele frequency (χ2 test). The 88K SNP panel captures ∼30% and the 41K panel ∼18% of common HapMap variants at an r2 > 0.80. (c) 41K SNP panel (>99% call rate), with correction for population stratification with PLINK CMH. Few non-MHC SNPs are observed in the tail of the statistical distribution, and λGC = 1.04, indicating adequate control of bias. (d,e) 80K SNP panel (>95% call rate) in unrelated FHS controls (d) and related FHS controls (e), obtained by applying a linear model fit for missing data and minor allele frequency interaction (dynamic genomic control). MHC SNPs have been excluded, and correction for population stratification has been applied with PLINK CMH. After applying dynamic genomic control (red diamonds), few non-MHC SNPs are observed in the tail of the statistical distribution, and λGC = 1.08. A similar pattern is observed in analysis of related individuals (and after correction for inflation due to relatedness among controls). Many (5 of 8) of the non-MHC SNPs with P < 10−5 were rare alleles (MAF < 0.05). In contrast, when call rate is uncorrected by the linear model, deviation from the null is observed at P < 0.01. The 80K SNP panel captures ∼29% of common HapMap variants.
